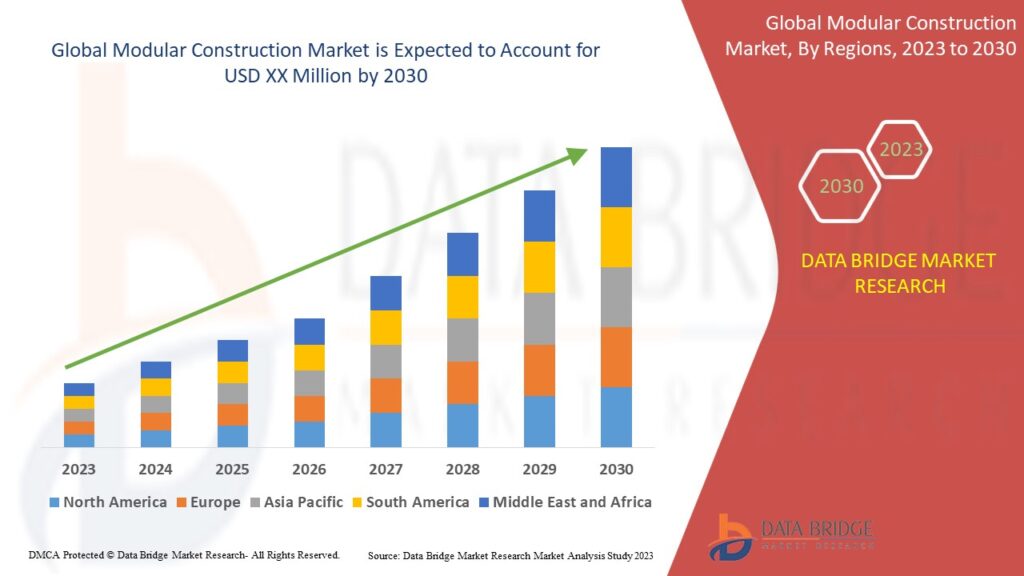
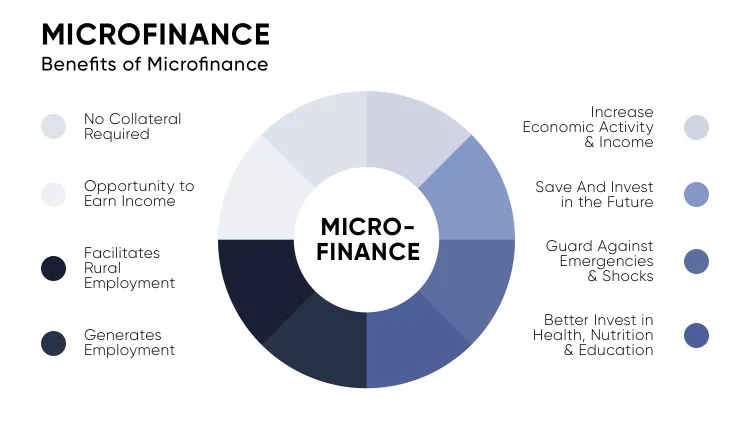
What You Need to Know About Sewage Water Recycling?

Ever wondered how sewage water recycling works and why it’s gaining so much attention? With growing concerns about water scarcity and pollution, recycling sewage water services is a game-changer for sustainable living. This guide explores everything you need to know about this transformative practice, from its benefits to its technologies and challenges.
Understanding Sewage Water Recycling
What is Recycled Sewage Water?
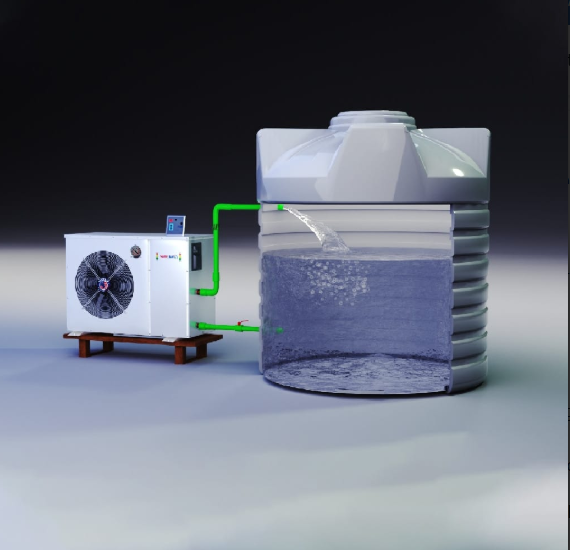
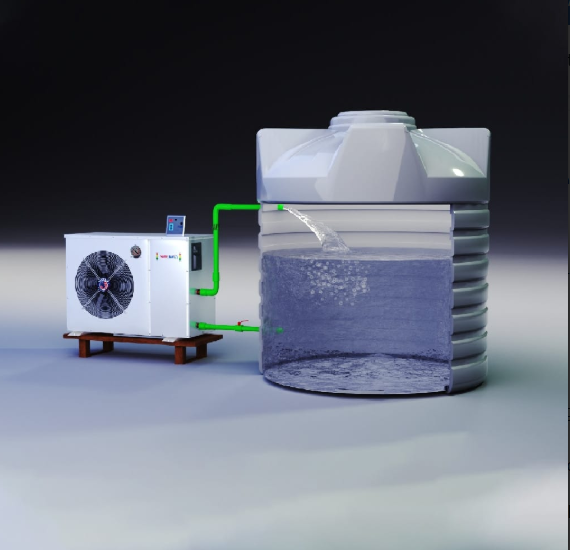
Recycled sewage water tanker services is wastewater that has been treated and purified to remove contaminants, making it suitable for specific uses like irrigation, industrial processes, or even drinking in some cases.
The Stages of Sewage Recycling
- Preliminary Treatment: Removes large debris and sediment.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological processes break down organic matter.
- Advanced Purification: Technologies like reverse osmosis and UV disinfection ensure high-quality water.
The Difference Between Treated and Recycled Water
Treated water is safe for discharge into the environment, while recycled water is specifically purified for reuse in various applications.
The Benefits of Sewage Water Recycling
Conserving Freshwater Resources
By reusing wastewater, we reduce the pressure on freshwater sources like rivers and lakes.
Reducing Environmental Pollution
Proper recycling prevents untreated sewage from contaminating natural ecosystems.
Supporting Sustainable Agriculture
Recycled water is rich in nutrients, making it ideal for irrigation in farming.
Mitigating the Effects of Water Scarcity
In water-stressed regions, recycling provides a reliable and sustainable solution.
Applications of Recycled Sewage Water
Agricultural Irrigation
Farmers use recycled water to nourish crops, promoting food security without depleting freshwater supplies.
Industrial Processes
Industries utilize recycled water for cooling systems and other non-potable uses, reducing their environmental footprint.
Landscape and Recreational Uses
Parks, golf courses, and fountains often rely on recycled water for maintenance and aesthetic appeal.
Groundwater Recharge
Recycled water can replenish aquifers, ensuring long-term water availability.
Technologies Used in Sewage Water Recycling
Membrane Bioreactors (MBR)
This technology combines biological treatment and membrane filtration for high-efficiency purification.
Reverse Osmosis (RO)
RO systems remove dissolved salts and contaminants, producing water of exceptional quality.
Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection
UV light neutralizes pathogens, ensuring the water is safe for reuse.
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs)
AOPs use powerful chemical reactions to degrade even the toughest pollutants.
Addressing Common Concerns
Is Recycled Water Safe?
Absolutely! When treated to stringent standards, recycled water is safe for its intended uses, including drinking in some cases.
How Is It Different from Potable Water?
Recycled water is tailored for specific applications, while potable water is treated for direct human consumption.
What About the Costs Involved?
While initial investments can be high, long-term savings and environmental benefits outweigh the costs.
Challenges in Sewage Water Recycling
Infrastructure Limitations
Outdated or insufficient systems can hinder recycling efforts.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Overcoming the “yuck factor” is crucial for widespread adoption.
High Initial Investment Costs
Installing advanced treatment technologies requires significant funding.
Treatment of Emerging Contaminants
Pharmaceutical residues and microplastics present unique challenges for recyclers.
Sewage Recycling and Sustainability
Aligning with the Circular Economy
Recycling water embodies the principles of reuse, reducing waste, and creating a sustainable cycle.
Reducing Carbon Footprints
Efficient recycling processes lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional water sourcing methods.
Enhancing Water Security
A steady supply of recycled water strengthens resilience against droughts and water shortages.
Steps to Promote Sewage Water Recycling
Raising Awareness and Education
Public campaigns and educational programs can demystify the process and benefits of recycling.
Implementing Supportive Policies
Governments can incentivize recycling projects through grants and tax breaks.
Encouraging Innovation in Technology
Investment in R&D will lead to more efficient and cost-effective recycling methods.
Public-Private Partnerships
Collaboration between governments and businesses can scale up recycling efforts globally.
Conclusion
Sewage water recycling is more than just a technological solution—it’s a lifeline for our planet. By conserving resources, reducing pollution, and supporting sustainable practices, it plays a pivotal role in addressing global water challenges. Embracing recycling isn’t just a necessity; it’s a step toward a brighter, water-secure future.
FAQs
- What is sewage water recycling?
It’s the process of treating wastewater to make it suitable for reuse in various applications. - Is recycled water safe for everyday use?
Yes, when treated to appropriate standards, it’s safe for uses like irrigation, industrial processes, and even drinking in some cases. - What technologies make sewage recycling effective?
Technologies like membrane bioreactors, reverse osmosis, and UV disinfection are key. - How does recycling sewage water support sustainability?
It conserves freshwater, reduces pollution, and provides a reliable resource in water-scarce areas. - What role can individuals play in promoting sewage water recycling?
By supporting policies, reducing waste, and advocating for local recycling initiatives, everyone can contribute.
Thanks for visiting onlinetechlearner


 English
English