Overcoming Challenges in Cloud Security Implementation

Introduction
Cloud computing has completely changed how businesses function in the digital age. Its scalability, flexibility, and accessibility have made it an indispensable tool for organizations of all sizes. However, with the convenience of cloud computing comes the challenge of ensuring robust security measures are in place. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, the need to address and overcome cloud security challenges becomes paramount. In this article, we’ll explore some of the key challenges faced in cloud security implementation and strategies to overcome them.
Definition
The methods and procedures used to safeguard infrastructure, data, and apps that are housed and used in cloud environments are together referred to as cloud security. It includes protections against data breaches, illegal access, and other dangers, guaranteeing the privacy, availability, and integrity of cloud resources. Identity and access control, encryption, frequent audits, and adherence to best practices are all necessary for effective cloud security.
Why Cloud Security Matters
Cloud computing offers unparalleled benefits, such as scalability, cost-efficiency, and accessibility. However, these advantages come with potential risks, including data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance issues. Ensuring cloud security is essential to:
Protect Sensitive Data: Prevent unauthorized access to personal, financial, and business-critical information.
Maintain Business Continuity: Minimize disruptions caused by security incidents.
Meet Compliance Requirements: Adhere to legal and regulatory standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
Preserve Trust: Safeguard your organization’s reputation by preventing data breaches.
Challenges in Cloud Security Implementation
Data Breaches and Privacy Concerns:
One of the most pressing challenges in cloud security is protecting sensitive data from breaches. With multiple users and organizations accessing shared resources, maintaining data privacy and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA becomes complex. Misconfigurations in security settings often leave sensitive information vulnerable.
Lack of Visibility and Control:
Organizations moving to the cloud often face reduced visibility and control over their data and infrastructure. Unlike on-premise systems, where IT teams have complete oversight, cloud environments are managed by third-party providers, creating blind spots in monitoring and security.
Misconfigurations and Human Errors:
Improperly configured cloud resources are a leading cause of security incidents. Errors in setting permissions, access controls, or storage configurations can expose systems to unauthorized access, leaving organizations vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Shared Responsibility Model:
Cloud providers operate under a shared responsibility model, where they handle the security of the cloud infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data and applications. This division can create confusion and gaps in security measures, especially for organizations unfamiliar with the model.
Evolving Threat Landscape:
The rapid evolution of cyber threats presents another significant challenge. Hackers are continually developing sophisticated methods to exploit cloud vulnerabilities, such as malware targeting virtual environments, account hijacking, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
Ensuring compliance with various regulatory standards is a critical challenge. Different industries and regions impose specific data protection laws, which require organizations to implement tailored security measures in their cloud infrastructure to avoid penalties and maintain trust.
Securing Multi-Cloud Environments:
Many organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in and improve flexibility. However, managing security across multiple platforms with different architectures and security protocols increases complexity, requiring specialized expertise and tools.
Cost of Advanced Security Measures:
Implementing advanced security measures in the cloud, such as encryption, intrusion detection systems, and robust access management, can be expensive. Smaller organizations often struggle to allocate adequate resources, leaving them exposed to risks.
The Role of Encryption in Cloud Security
Protecting Data at Rest and in Transit:
Encryption secures data both at rest (stored in cloud servers) and in transit (moving between users and cloud applications). Data at rest is protected through encryption algorithms that make it unreadable without the correct decryption key. Similarly, encrypting data in transit prevents interception by cybercriminals, ensuring secure communication over networks.
Preventing Unauthorized Access:
Encryption acts as a barrier against unauthorized access, even if cybercriminals breach cloud security defenses. Without the correct encryption key, stolen or leaked data remains useless to attackers. This added layer of security is particularly important for businesses handling sensitive customer information, financial records, or intellectual property.
Compliance with Security Regulations:
Many industries require strict compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Encryption helps organizations meet these requirements by ensuring that sensitive data is securely stored and transmitted. Failure to implement encryption could lead to legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
Enhancing User Trust and Privacy:
With growing concerns about data privacy, encryption reassures users that their information is secure in the cloud. Companies that prioritize encryption demonstrate a commitment to protecting user data, fostering trust among customers and stakeholders. This trust is essential for maintaining strong business relationships and brand reputation.
Future Trends of Cloud Security
AI-Powered Threat Detection:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing a pivotal role in enhancing cloud security. These technologies enable advanced threat detection by analyzing patterns, predicting vulnerabilities, and identifying anomalies in real-time, offering a proactive approach to securing cloud environments.
Zero Trust Architecture:
Zero trust is becoming a cornerstone of cloud security strategies. This approach enforces strict access controls, continuously verifying users and devices regardless of their location, minimizing the risk of data breaches in a perimeter-less cloud environment.
Security Automation:
Automation tools are revolutionizing cloud security by simplifying compliance, improving incident response times, and reducing human error. Automated processes, like vulnerability scanning and patch management, are expected to become increasingly prevalent.
Multi-Cloud Security Solutions:
As organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies, ensuring consistent security across multiple providers is critical. Unified security platforms that integrate seamlessly across clouds will gain traction, simplifying governance and risk management.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE):
SASE is emerging as a popular framework that integrates network security and wide-area networking (WAN). This trend focuses on providing secure, seamless access for remote users while maintaining strong cloud data protection.
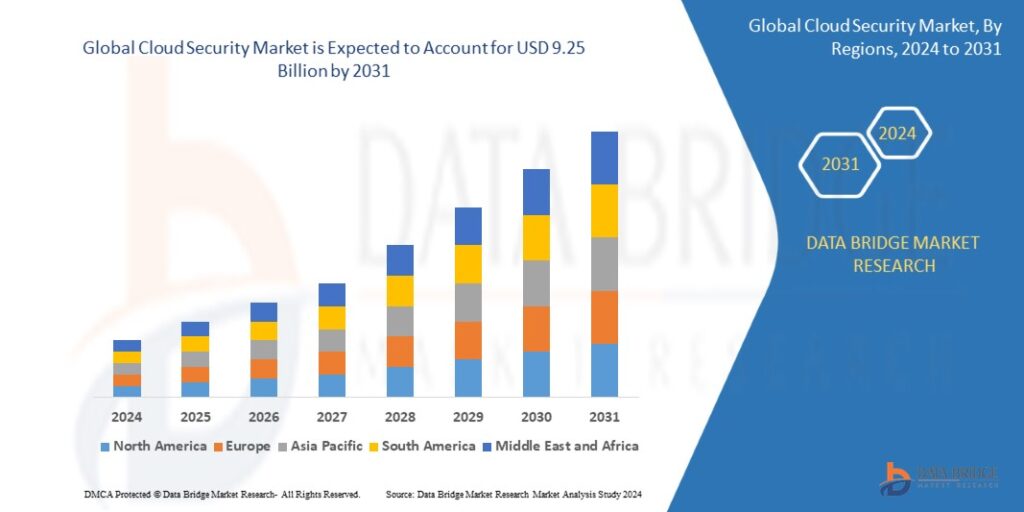
Growth Rate of Cloud Security Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research’s analysis, the global cloud security market is predicted to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.2% between 2024 and 2031, from its estimated valuation of USD 2.2 billion in 2023 to USD 9.25 billion by 2031.
To read more click here.
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cloud-security-market
Conclusion
While the benefits of cloud computing are undeniable, ensuring the security of cloud environments remains a critical concern for businesses. By understanding the challenges associated with cloud security implementation and adopting proactive strategies, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and safeguard their data and resources in the cloud. From comprehensive risk assessments to leveraging advanced security solutions, addressing cloud security challenges requires a multifaceted approach. By prioritizing security and staying vigilant, businesses can confidently harness the power of the cloud while minimizing security risks.


 English
English 


















































































































































































































































































































 Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses
Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses