Modular Construction: Revolutionizing the Future of Building
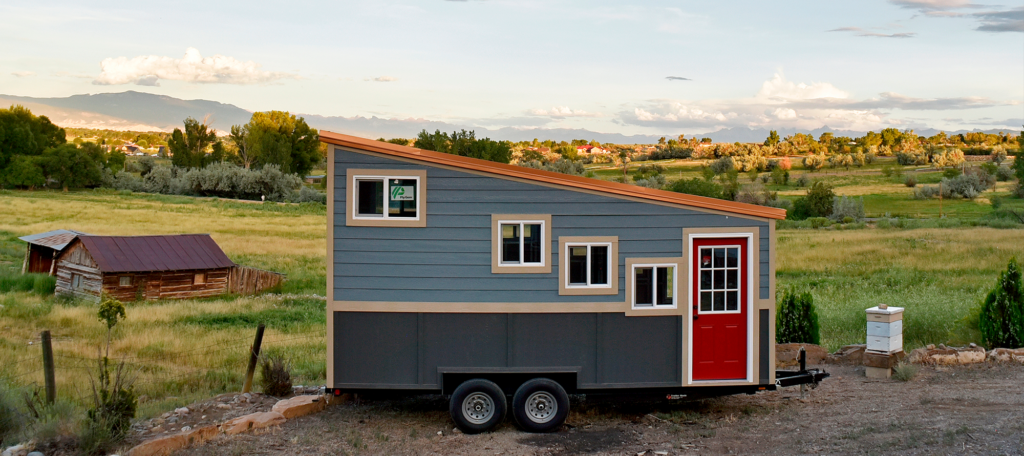
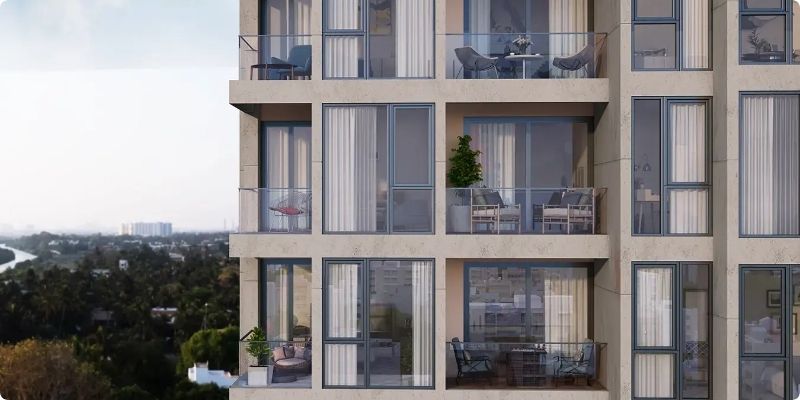
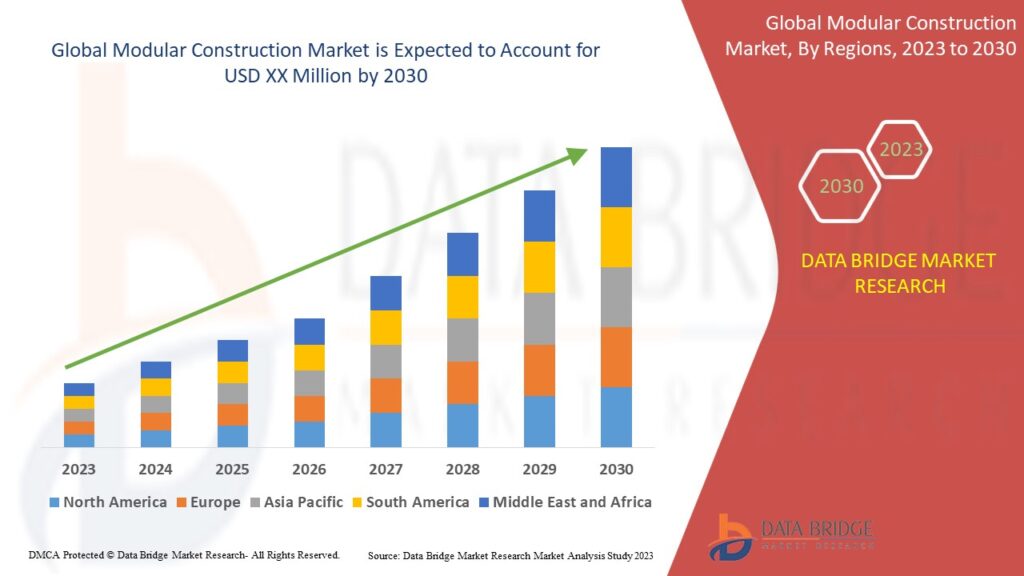
Modular construction is rapidly transforming the global construction landscape. By leveraging factory-produced components that are assembled on-site, this innovative building method offers speed, efficiency, and sustainability, making it an attractive choice for a wide range of construction projects. From residential homes to large-scale commercial buildings, modular construction is paving the way for a smarter and more efficient future in the industry.
In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of modular construction, its benefits, key applications, and the trends shaping its growth.
What is Modular Construction?
Modular construction involves the prefabrication of building components, known as modules, in a controlled factory environment. These modules are then transported to the construction site and assembled into the final structure. Unlike traditional construction methods that rely heavily on on-site work, modular construction streamlines the process by handling most of the work off-site.
Modules are fully customizable and can include walls, floors, ceilings, and even pre-installed electrical and plumbing systems. They are designed to fit together seamlessly, creating structures that are indistinguishable from those built using conventional methods.
Types of Modular Construction
1. Permanent Modular Construction (PMC)
- Description: Modules are prefabricated and permanently installed at the construction site.
- Applications: Hotels, schools, hospitals, and office buildings.
- Key Feature: Offers long-lasting, durable structures that adhere to local building codes.
2. Relocatable Modular Construction (RMC)
- Description: Temporary or semi-permanent modules designed for easy relocation.
- Applications: Construction site offices, disaster relief housing, and event spaces.
- Key Feature: Focuses on flexibility and mobility.
Key Benefits of Modular Construction
1. Faster Construction Times
- Prefabrication in a factory allows simultaneous on-site preparation and module manufacturing.
- Speeds up project completion by 30-50% compared to traditional methods.
2. Cost Efficiency
- Reduces labor costs by centralizing production in factories.
- Minimizes material waste through precision manufacturing processes.
3. Sustainability
- Utilizes eco-friendly materials and promotes recycling.
- Generates significantly less waste compared to traditional construction.
4. Enhanced Quality Control
- Factory-controlled environments ensure consistent quality.
- Reduces risks associated with weather delays or on-site errors.
5. Improved Safety
- Limits on-site construction work, reducing exposure to hazardous conditions.
- Promotes worker safety by centralizing production in monitored environments.
6. Design Flexibility
- Customizable modules can accommodate diverse architectural styles.
- Easily scalable for expanding or downsizing buildings.
Applications of Modular Construction
1. Residential Buildings
- Applications: Single-family homes, multi-family housing, and luxury apartments.
- Benefits: Faster move-in times and cost-effective customization.
2. Healthcare Facilities
- Applications: Hospitals, clinics, and emergency medical units.
- Benefits: Rapid deployment of facilities, especially during crises like pandemics.
3. Educational Institutions
- Applications: Classrooms, dormitories, and laboratories.
- Benefits: Quick setup for growing student populations.
4. Commercial Spaces
- Applications: Retail stores, office spaces, and restaurants.
- Benefits: Adaptable designs that cater to business needs.
5. Hospitality Industry
- Applications: Hotels, resorts, and vacation rentals.
- Benefits: Speedy construction without compromising quality.
6. Industrial Projects
- Applications: Warehouses, factories, and data centers.
- Benefits: Cost-effective solutions for large-scale operations.
Technological Advancements in Modular Construction
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
- Enhances design accuracy by creating detailed 3D models.
- Facilitates collaboration between architects, engineers, and contractors.
2. Robotics and Automation
- Automates repetitive tasks in factory production, improving efficiency.
- Reduces labor requirements and production timelines.
3. Advanced Materials
- Incorporates lightweight, durable materials like cross-laminated timber (CLT) and high-performance concrete.
- Improves energy efficiency and structural integrity.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
- Integrates smart sensors to monitor construction processes.
- Enables real-time tracking of module transportation and installation.
Challenges in Modular Construction
1. Transportation and Logistics
- Modules must be transported to the site, which can be challenging for remote locations or urban areas with narrow roads.
2. Initial Investment Costs
- High upfront costs for factory setup and equipment can deter smaller firms.
3. Limited Awareness
- Traditional builders and clients may be unfamiliar with modular methods, creating resistance to adoption.
4. Design Constraints
- While customizable, modules must adhere to size limitations for transportation, which can limit design possibilities.
Global Trends
1. Rising Demand for Affordable Housing
- Governments and developers are leveraging modular construction to address housing shortages.
2. Sustainability Focus
- Growing emphasis on green building practices is driving the adoption of modular methods.
3. Urbanization
- Increased urban population density necessitates faster and more efficient construction methods.
4. Integration with Smart Technology
- Smart buildings with IoT-enabled modules are becoming more popular in commercial and residential sectors.
5. Expansion in Emerging Markets
- Countries in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America are adopting modular construction to meet infrastructure demands.
Future
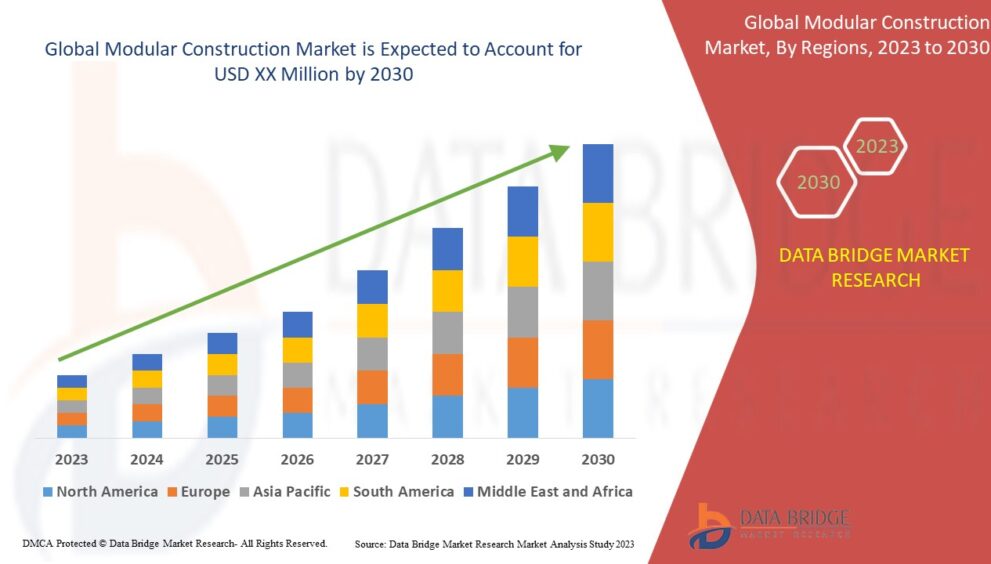
The modular construction market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and the need for sustainable building solutions. As the industry evolves, we can anticipate innovations such as:
- 3D-Printed Modules: Additive manufacturing techniques to create customized modules.
- Carbon-Neutral Factories: Facilities powered by renewable energy to reduce the environmental footprint.
- Increased Automation: Use of AI and robotics to streamline production processes.
Tips for Adopting Modular Construction
- Collaborate Early: Engage architects, engineers, and manufacturers from the project’s inception.
- Plan Logistics: Ensure seamless transportation and installation of modules.
- Focus on Compliance: Adhere to local building codes and regulations.
- Evaluate ROI: Assess long-term savings in time, labor, and maintenance.
- Leverage Technology: Use BIM and project management tools for efficient planning.
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-modular-construction-market
Conclusion
Modular construction is not just a trend but a transformative approach to building. By offering faster, greener, and more cost-effective solutions, it is redefining how we construct homes, offices, and infrastructure. As urbanization and sustainability take center stage, modular construction is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the construction industry.


 English
English 


















































































































































































































































































































 Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses
Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses