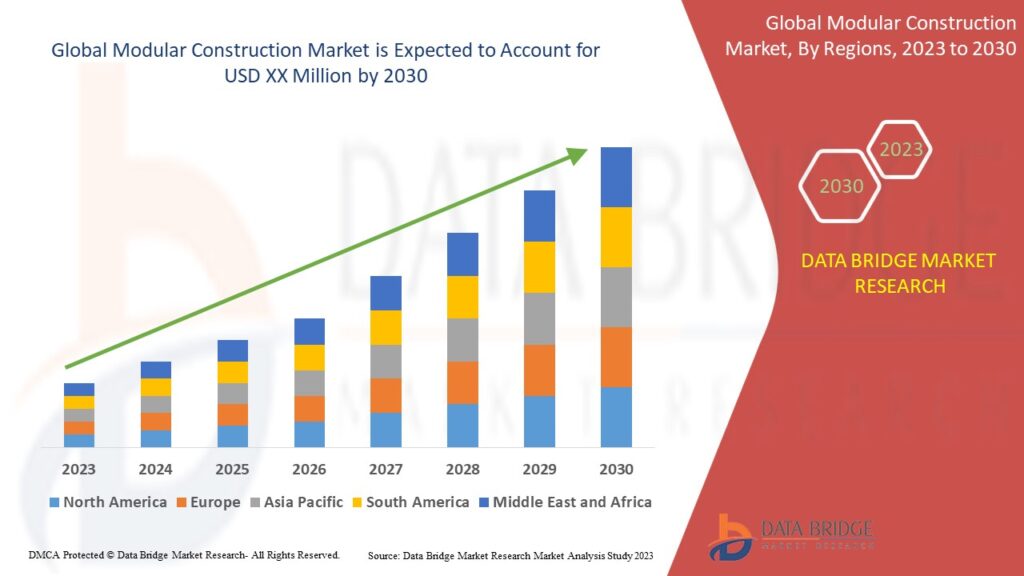
How Do Chemical Beakers Differ from Regular Glass Containers?

1. Introduction to Chemical Beakers and Regular Glass Containers
At first glance, a chemical beaker might resemble a simple glass jar or cup, but they serve vastly different purposes. While regular glass containers are used in kitchens or for storage, chemical beakers are precision tools specifically designed for laboratory work. Understanding their unique features is crucial for anyone venturing into scientific or industrial applications.
2. Material Composition: Specialized Glass vs. Ordinary Glass
One of the key differences lies in the material used to manufacture these items:
- Chemical Beakers: Most chemical beakers are made from borosilicate glass, a type of glass engineered for high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Borosilicate glass is composed of silica and boron trioxide, making it highly durable under extreme conditions.
- Regular Glass Containers: These are typically made from soda-lime glass, the most common form of glass used in household items. Soda-lime glass is less expensive but lacks the same resistance to heat and chemicals.
Why Does This Matter?
The material composition impacts the beaker’s ability to withstand the high temperatures and corrosive chemicals often encountered in labs. Regular glass containers may crack or degrade under such conditions.
3. Design Differences and Features
Shape and Structure
Chemical beakers have a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom, designed for stability and ease of use during experiments. The walls are usually thicker compared to regular glass containers, enhancing durability.
Regular glass containers, on the other hand, come in various shapes and sizes—from jars to cups—and are optimized for aesthetics and general usability rather than scientific precision.
Measurement Markings
Beakers are often marked with graduated measurement lines to indicate volume. While these markings are not as precise as those on a graduated cylinder, they provide a convenient way to measure liquids during experiments.
Regular glass containers rarely include measurement markings, as they are not designed for precision measurements.
Pouring Spouts
Most chemical beakers feature a small spout for easy and controlled pouring of liquids. This is crucial in lab settings to prevent spills and ensure accuracy.
In contrast, regular glass containers may or may not include a spout, and if they do, the design is usually more basic.
4. Durability and Resistance
Heat Resistance
Borosilicate glass used in chemical beakers can withstand high temperatures without cracking, making it ideal for experiments involving heat. Some beakers are even designed to be used directly over open flames or hot plates.
Regular glass containers, made from soda-lime glass, have a much lower tolerance for heat. Sudden temperature changes can cause them to shatter.
Chemical Resistance
Chemical beakers are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This ensures that the container does not react with the substances inside, maintaining the integrity of experiments.
Regular glass containers may react with certain chemicals, making them unsuitable for laboratory use.
Impact Resistance
Although borosilicate glass is highly durable, it is not indestructible. It can resist minor impacts but may break if dropped from a height. Regular glass containers are generally less durable and more prone to chipping or breaking upon impact.
5. Intended Uses: Scientific vs. Everyday Applications
- Chemical Beakers: These are specifically designed for laboratory tasks such as mixing, heating, and measuring chemicals. Their design and material make them indispensable in scientific research, education, and industrial processes.
- Regular Glass Containers: These are intended for everyday uses such as storing food, holding beverages, or decorative purposes. They lack the specialized features needed for scientific applications.
6. Safety Considerations
Handling Chemicals
Using the right container is critical for safety. Chemical beakers are designed to safely handle corrosive and hazardous substances, while regular glass containers can pose risks when exposed to such materials.
Temperature Fluctuations
Borosilicate glass’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes makes chemical beakers much safer for heating and cooling processes. Regular glass containers, however, are prone to thermal shock, which can lead to dangerous breakages.
7. Cost and Availability
Chemical beakers are generally more expensive than regular glass containers due to their specialized materials and design. However, they are widely available through laboratory supply stores and online retailers. Regular glass containers are inexpensive and can be found in grocery stores, home goods shops, and online marketplaces.
8. Examples of Use in Laboratories
Common Experiments
- Mixing Solutions: Beakers are commonly used for preparing chemical solutions by mixing multiple substances.
- Heating Liquids: Beakers can be placed on Bunsen burners or hot plates for heating.
- Chemical Reactions: They are often the go-to choice for observing small-scale reactions.
Specialized Tasks
Some experiments, like titration, require more precise instruments, but beakers are frequently used in the preparatory steps.
9. Comparison Table: Chemical Beakers vs. Regular Glass Containers
| Feature | Chemical Beakers | Regular Glass Containers |
| Material | Borosilicate Glass | Soda-Lime Glass |
| Heat Resistance | High | Low |
| Chemical Resistance | High | Low |
| Durability | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Shape | Cylindrical with Flat Bottom | Varies (jars, cups, etc.) |
| Markings | Graduated Measurement Lines | Rarely Present |
| Pouring Spout | Yes | Sometimes |
| Intended Use | Laboratory Experiments | Everyday Applications |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
10. Conclusion
While chemical beakers and regular glass containers may look alike to the untrained eye, their differences are substantial. Chemical beakers are precision-engineered for laboratory use, offering superior heat resistance, chemical durability, and practical design features like measurement markings and pouring spouts. Regular glass containers, on the other hand, are designed for general household use and lack the specialized features needed for scientific applications.
Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone working with chemicals or conducting experiments. Using the right container not only ensures accuracy but also significantly enhances safety and efficiency in the laboratory.certifiedmtp.com of different models, you can ensure that you invest in a benchtop oven that meets your needs and exceeds your expectations.


 English
English 


















































































































































































































































































































 Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses
Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses