How Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Helps Neurological Disorders

Neurological disorders can often be disabling, affecting movement, speech, and overall quality of life. While medications can help manage these conditions, they aren’t always effective for everyone. Deep brain stimulation surgery (DBS) is a treatment option that has shown significant promise in managing symptoms of certain neurological disorders, especially when medications fail. Here is a detailed guest post of how this surgery works and how it helps improve the lives of those with chronic neurological conditions.
What is Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery?
Deep brain stimulation surgery involves implanting small electrodes into specific parts of the brain. These electrodes are connected to a device implanted in the chest, much like a pacemaker. The device sends electrical impulses to the brain, helping to regulate abnormal brain activity associated with neurological disorders. This stimulation alters the way brain cells communicate, easing the symptoms of conditions like Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. Unlike other forms of surgery that may be irreversible, deep brain stimulation surgery can be adjusted or even turned off if necessary. This flexibility makes it a particularly attractive option for patients who have not found relief from other treatments.
Conditions Treated by Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
Deep brain stimulation surgery is primarily used for disorders that affect motor function, including:
- Parkinson’s Disease: One of the most common uses of DBS is for Parkinson’s disease, which causes tremors, stiffness, and slow movements. By stimulating the brain, DBS helps alleviate these symptoms, enabling patients to move more freely and live more independently.
- Essential Tremor: This condition causes uncontrollable shaking, particularly in the hands. DBS can significantly reduce these tremors, helping patients perform daily tasks more easily.
- Dystonia: Dystonia involves involuntary muscle contractions that cause twisting and repetitive movements. DBS can help manage these muscle spasms and provide relief.
- Epilepsy: For patients who suffer from seizures that don’t respond to medication, deep brain stimulation surgery may offer another way to control and reduce seizure activity.
These disorders can make everyday activities challenging, but DBS offers a way to manage the symptoms when other treatments haven’t worked.
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work?
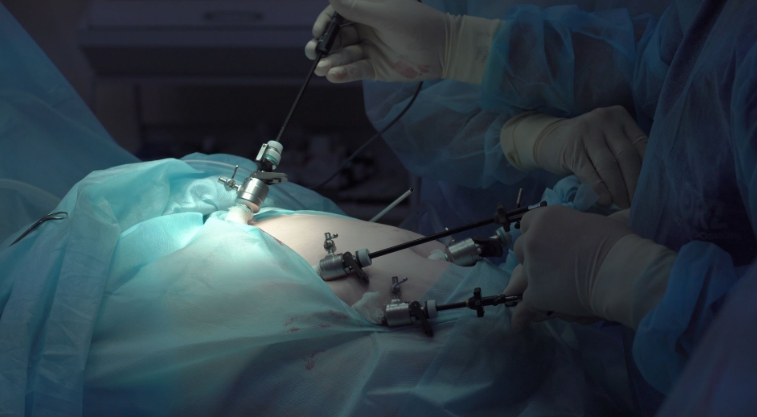
The key to deep brain stimulation surgery is the implantation of electrodes in targeted areas of the brain. The electrodes are connected to a pulse generator, which is surgically placed under the skin near the collarbone. The pulse generator sends electrical signals to the brain, helping to regulate the abnormal electrical activity associated with neurological disorders. The settings of the pulse generator can be adjusted externally. Doctors can increase or decrease the intensity and frequency of the electrical impulses to ensure the best possible outcome for each patient. This customisation allows for precise treatment based on the individual’s needs and symptoms. The surgery itself is minimally invasive, and patients typically recover quickly. In many cases, the procedure is done while the patient is awake so doctors can monitor their responses and fine-tune the system during the process.
Benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
Deep brain stimulation surgery has several benefits for patients dealing with chronic neurological disorders:
- Improved Motor Function: One of the most immediate benefits of DBS is the improvement in motor function. Patients with Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and other movement disorders often experience significant relief from symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and slow movements.
- Reduced Medication Dependence: Many patients who undergo DBS find they can reduce their reliance on medications, which often come with side effects. With DBS, patients can manage their symptoms more effectively with lower doses of medication.
- Reversibility and Flexibility: Unlike some other surgeries, DBS is reversible. If a patient experiences adverse effects or if the device needs adjustment, doctors can modify the settings or turn off the device entirely. This flexibility is an important advantage over permanent surgical options.
- Long-Term Effectiveness: The effects of deep brain stimulation surgery can be long-lasting. Patients often experience sustained improvement in their symptoms over time, although regular check-ups are necessary to adjust the settings as needed.
Risks and Considerations
Like any surgery, deep brain stimulation surgery comes with some risks. While the procedure itself is relatively safe, potential complications can include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Stroke
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
Additionally, some patients may experience side effects from the electrical stimulation, including speech difficulties, balance issues, or mood changes. However, most of these side effects can be managed or resolved with adjustments to the stimulation settings. It’s also important to note that DBS doesn’t cure neurological disorders. Instead, it helps manage the symptoms. For patients, this means they can experience a better quality of life, but ongoing care and follow-up are still essential.
Know more about : Brain Surgery For Children: How It Works?
Conclusion
Deep brain stimulation surgery offers a promising solution for people with neurological disorders that have not responded to medication. It can improve motor function, reduce medication dependency, and offer flexibility in treatment. Although the surgery carries some risks, its benefits in terms of symptom management and quality of life are significant. For many, DBS is a life-changing option that helps them regain control over their symptoms and lead a more active, independent life. As medical technology continues to advance, treatments like DBS are providing hope for patients dealing with chronic neurological conditions.


 English
English