Difference Between A2 Ghee and Clarified Butter

Ghee and clarified butter are both popular ingredients in Indian kitchens and beyond. While they may seem similar, they differ in preparation, properties, and benefits. This blog delves into the key distinctions between the two, helping you understand their unique characteristics and uses.
What is Clarified Butter?
Clarified butter is made by heating butter until the water content evaporates, and the milk solids separate from the fat. The clear, golden liquid fat is strained, leaving behind the milk solids. Its neutral flavour makes it versatile for cooking various dishes, especially in cuisines requiring high-heat cooking.
Clarified butter is commonly used in Western recipes for sautéing, frying, and baking. Its simplicity in flavour allows it to blend seamlessly into many dishes without overpowering other ingredients.
What is A2 Ghee?
A2 Ghee is a type of ghee made from the milk of cows that produce the A2 beta-casein protein, such as indigenous Indian breeds like Gir and Sahiwal. The process of making A2 ghee involves traditional methods, typically using cultured butter or curd made from cow’s milk. It is slowly heated, ensuring the preservation of its nutritional benefits.
A2 Ghee is deeply rooted in Indian culture and is often considered a superfood due to its health-promoting properties. It is commonly used in cooking, religious rituals, and Ayurveda for its medicinal qualities.
Key Differences Between A2 Ghee and Clarified Butter
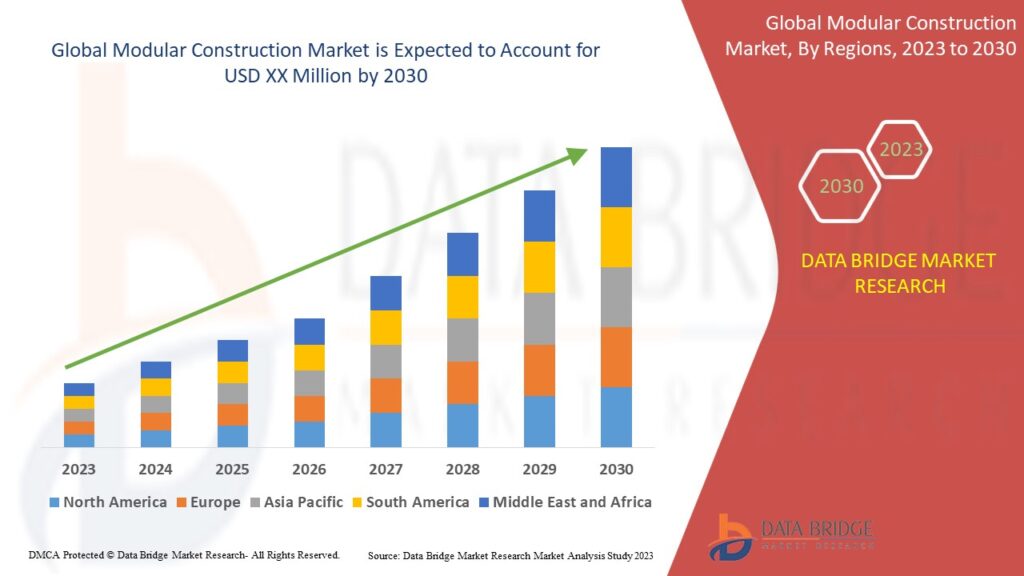
1. Source of Milk
- Clarified Butter: Made from regular butter, which may come from cows, buffaloes, or mixed sources. The type of milk used is not specific.
- A2 Ghee: Exclusively made from A2 cow’s milk, derived from specific Indian cow breeds. This gives it a more distinct and traditional origin.
2. Nutritional Profile
- Clarified Butter: Contains healthy fats and is free from milk solids, but it lacks the unique benefits of A2 protein.
- A2 Ghee: Packed with A2 beta-casein protein, vitamins (like A, D, E, and K), and Omega-3 fatty acids. It is believed to be easier to digest and beneficial for those with lactose intolerance.
3. Preparation Process
- Clarified Butter: Prepared by melting and straining butter, a relatively quick process.
- A2 Ghee: Made using traditional methods where milk is converted into curd, churned to extract butter, and then slow-cooked to produce ghee. This process enhances its aroma, flavour, and nutritional value.
4. Cultural Significance
- Clarified Butter: Widely used in Western cuisines for cooking and baking. It has limited cultural or medicinal significance.
- A2 Ghee: Holds a revered place in Indian households, used in religious offerings, Ayurvedic treatments, and traditional recipes. It is often considered sacred and used in lamps during festivals.
5. Taste and Aroma
- Clarified Butter: Neutral in taste with a light buttery aroma. It does not have the depth of flavour found in ghee.
- A2 Ghee: Rich, nutty, and aromatic. Its flavour enhances the taste of traditional Indian dishes like khichdi, dal, and sweets.
6. Smoke Point
- Clarified Butter: Has a high smoke point (around 232°C), making it suitable for frying and sautéing at high temperatures.
- A2 Ghee: Also has a high smoke point (around 250°C) and is excellent for deep frying or tempering spices.
Health Benefits of A2 Ghee and Clarified Butter
1. A2 Ghee:
- Digestive Health: The presence of A2 protein and butyric acid promotes gut health and aids digestion.
- Boosts Immunity: Rich in antioxidants and fat-soluble vitamins, A2 cow ghee supports the immune system.
- Joint Health: Its anti-inflammatory properties help in reducing joint pain and improving flexibility.
- Energy Source: Provides a steady source of energy, making it ideal for athletes and active individuals.
2. Clarified Butter:
- Healthy Fats: Contains good fats that support heart and brain health when consumed in moderation.
- Lactose-Free: Suitable for those with lactose intolerance, as the milk solids are removed during preparation.
- Versatility: A versatile cooking fat that works well in various recipes, from savoury to sweet.
3. Culinary Uses
Both A2 ghee and clarified butter have their unique roles in cooking:
- Clarified Butter: Commonly used in Western dishes like sauces, pastries, and grilled items due to its mild taste and high smoke point.
- A2 Ghee: Integral to Indian cooking, it adds depth and aroma to curries, rice dishes, and desserts. It is also used in tempering spices to enhance flavour.
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between A2 ghee and clarified butter depends on your preferences, dietary needs, and the type of cuisine you’re preparing. If you prioritise traditional, health-focused options with cultural significance, A2 ghee is a great choice. On the other hand, if you need a neutral cooking fat for everyday use, clarified butter is a practical option.
Final Thoughts
While both A2 ghee and clarified butter have their merits, they cater to different needs and tastes. Understanding their differences allows you to make informed choices for your kitchen and health. Whether you’re cooking a hearty Indian meal or a delicate Western dish, selecting the right fat can elevate your culinary experience.


 English
English 


















































































































































































































































































































 Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses
Office Clearance for SMEs: Affordable Solutions Businesses