Discover New Builds in Easton: Modern Living

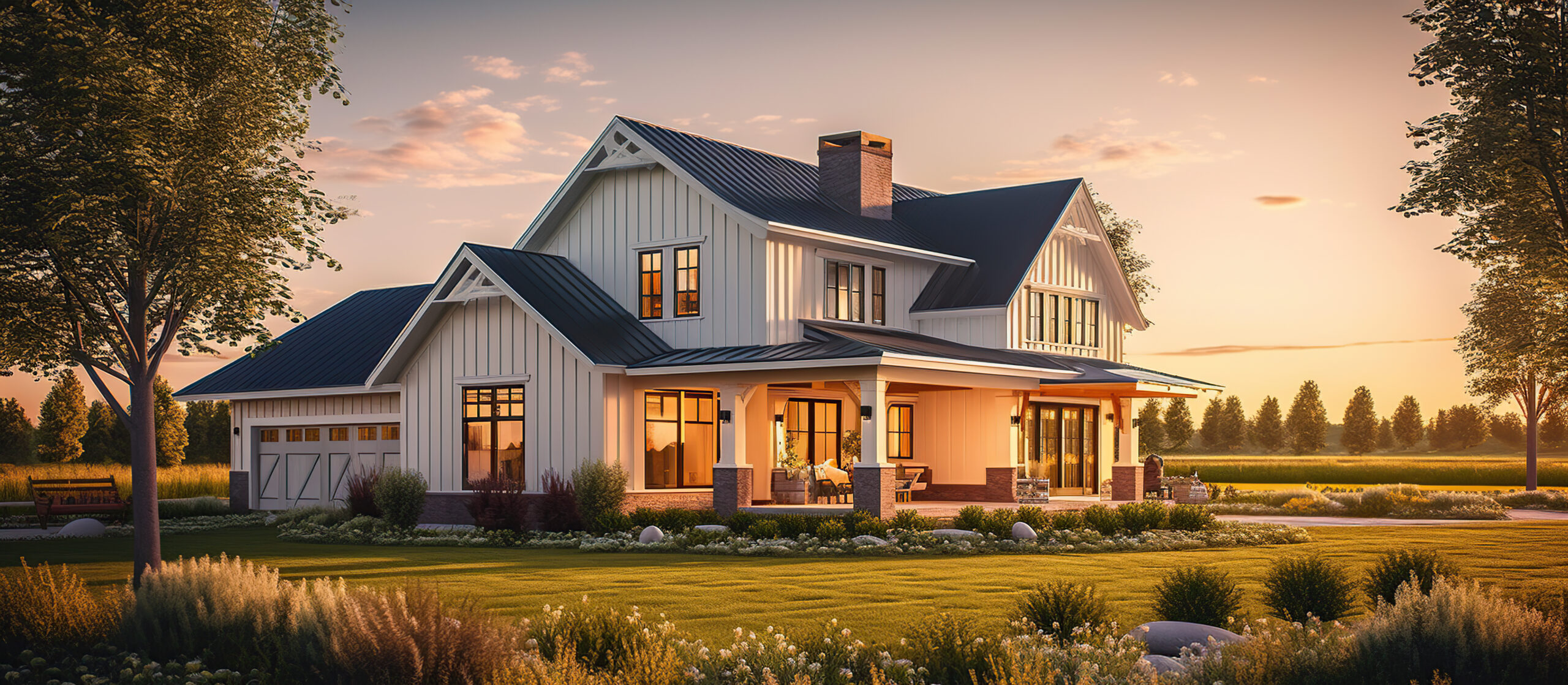
Easton, a picturesque village in Norfolk, is rapidly emerging as a sought-after destination for homebuyers seeking contemporary, sustainable homes. Combining rural serenity with excellent connectivity to Norwich and beyond, new builds in Easton provide an ideal setting for families, professionals, and retirees. If you’re searching for new builds near me or exploring new builds UK, Easton’s dynamic property market offers a wealth of opportunities. This guide highlights why Easton is the perfect place to call home, the advantages of new builds, and what makes this village a standout choice.
Why Easton is a Top Choice for New Builds
Nestled just off the A47, Easton offers a peaceful escape from urban hustle while remaining close to Norwich’s cultural and commercial hubs. New builds in Easton are designed with today’s homeowners in mind, featuring energy-efficient systems, modern layouts, and high-quality finishes. From stylish apartments to expansive family homes, these properties cater to a variety of preferences and budgets, making Easton a prime location for those seeking new builds near me.
The surge in demand for new builds UK reflects a growing preference for homes that blend sustainability with convenience. Easton’s developments deliver on both fronts, offering easy access to major roads, top-rated schools, and local amenities. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or looking to relocate, Easton’s blend of village charm and modern living is hard to resist.
Key Benefits of New Builds in Easton
Investing in a new build in Easton comes with significant advantages. Here’s why these homes are an excellent choice:
1. Superior Energy Efficiency
New builds in Easton are built to high environmental standards, incorporating features like advanced insulation, energy-efficient windows, and eco-friendly heating systems. These elements reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills, making them a cost-effective option. Many homes also include smart technology for controlling lighting and heating, enhancing both efficiency and comfort.
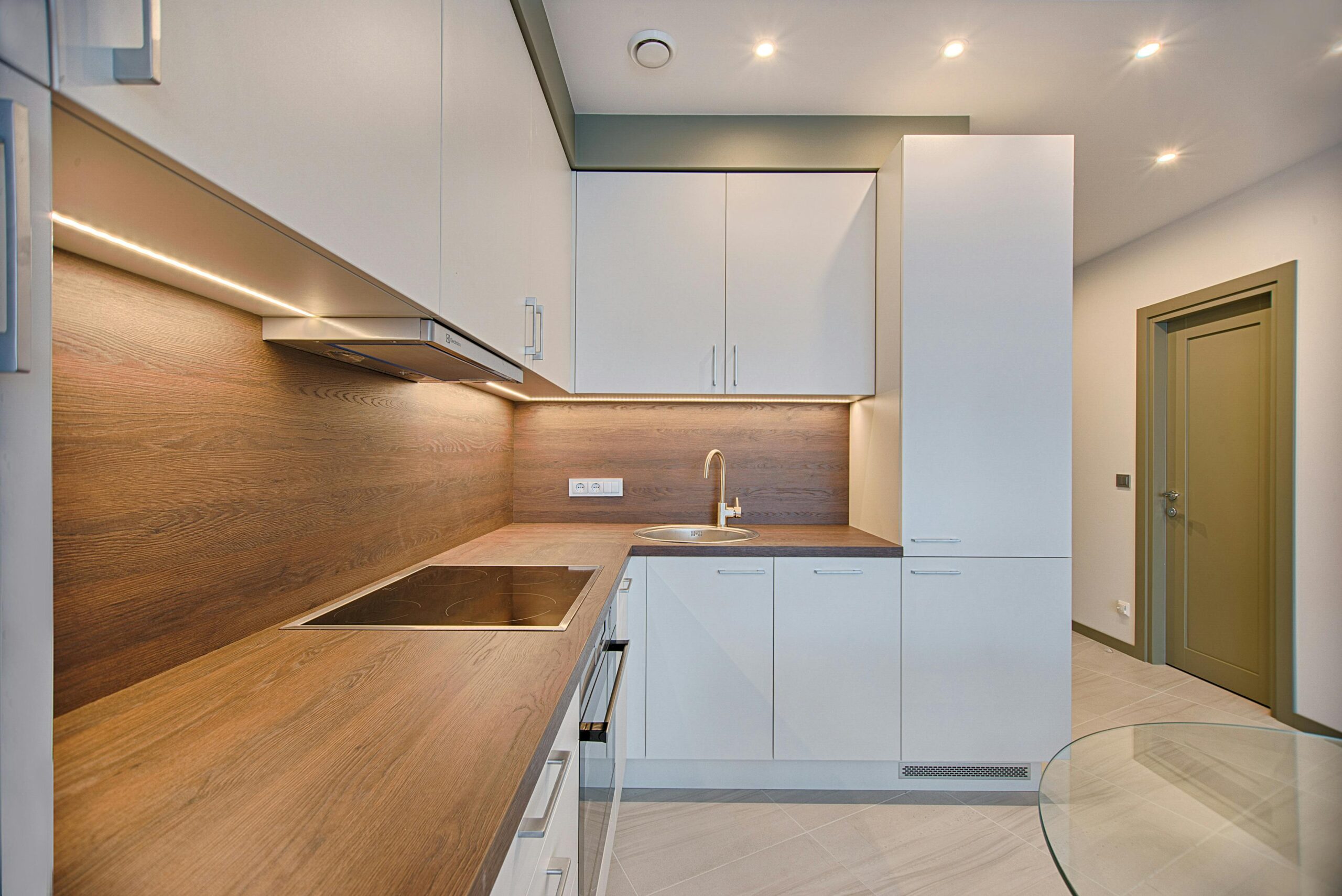
2. Modern, Customizable Designs
New builds offer spacious, open-plan layouts that maximize light and functionality. Homebuyers often have the chance to personalize their properties, selecting finishes like kitchen countertops or bathroom tiles to suit their taste. Whether you want a compact, low-maintenance home or a large family residence, Easton’s new builds provide flexibility and style.
3. Reduced Maintenance Costs
Constructed to the latest building regulations, new builds require minimal upkeep compared to older properties. High-quality materials and robust construction ensure long-term durability, while warranties, such as the 10-year NHBC guarantee, offer added peace of mind. This makes new builds in Easton a smart, low-maintenance investment.
4. Strong Community Focus
Easton’s new developments are designed to foster connection and community. Features like shared green spaces, playgrounds, and pedestrian-friendly pathways encourage outdoor activities and neighborly interaction. With local shops, schools, and recreational facilities nearby, residents enjoy a vibrant, family-oriented lifestyle.
Easton’s Growing Property Market
Easton’s property market is booming, driven by its affordability and strategic location. Compared to urban centers like London or Cambridge, new builds in Easton offer exceptional value, appealing to buyers seeking new builds UK. Developers are prioritizing sustainability, with many homes equipped with solar panels, electric vehicle charging stations, and water-saving systems to meet modern environmental standards.
Families are drawn to Easton for its access to excellent schools, including St Peter’s CofE Primary School and Easton & Otley College, both highly regarded for their academic programs. Professionals benefit from the village’s proximity to Norwich’s business districts and retail hubs, such as Longwater Retail Park, ensuring convenience without compromising on tranquility.
What to Expect from Easton’s New Builds
Choosing a new build in Easton means embracing a lifestyle that blends modern comfort with village charm. Here’s what sets these homes apart:
-
Spacious Interiors: Open-plan living areas, generous bedrooms, and private gardens create versatile spaces for relaxation and entertaining.
-
Smart Home Integration: Control security, heating, and lighting systems remotely, adding convenience and efficiency to everyday life.
-
Excellent Connectivity: Proximity to the A47 and Norwich’s train station makes commuting or exploring Norfolk effortless.
-
Local Conveniences: Village shops, pubs, and nearby retail parks provide everything you need for daily living.
Why Easton Stands Out
Easton’s unique appeal lies in its ability to offer rural tranquility alongside modern amenities. Norwich, just minutes away, boasts a vibrant cultural scene with theaters, galleries, and historic sites like Norwich Castle. Nature lovers can explore the Norfolk Broads or coastal gems like Cromer, both within an hour’s drive. In Easton itself, quiet lanes and green spaces create a welcoming environment for residents of all ages.
For families, Easton’s access to quality education and safe, community-focused neighborhoods is a major draw. Professionals appreciate the option to work remotely in a peaceful setting while staying connected to urban opportunities. Whether you’re searching for new builds near me or a long-term home, Easton delivers a lifestyle that balances work, leisure, and community.
Tips for Buying a New Build in Easton
If you’re considering a new build in Easton, these tips can help streamline your purchase:
-
Research Reputable Developers: Choose developers known for quality construction and reliable customer support. Verify warranty details.
-
Visit Showhomes: Touring a showhome allows you to assess the layout, materials, and overall feel of the property.
-
Explore Developer Incentives: Look for offers like stamp duty assistance or included appliances to reduce upfront costs.
-
Plan for Growth: Ensure the home meets your future needs, whether it’s extra bedrooms or space for a home office.
-
Secure Early: Easton’s new builds are highly sought-after, so reserving a property early can help you secure your ideal home.
The Future of New Builds in Easton
With growing interest in new builds UK, Easton is poised for continued expansion. Future developments will include more eco-friendly homes and community amenities, ensuring the village remains a top destination for modern homeowners. By prioritizing green technology and thoughtful design, Easton is setting a standard for sustainable living in 2025 and beyond.
Conclusion
New builds in Easton offer a unique opportunity to own a stylish, energy-efficient home in a thriving Norfolk village. With its scenic surroundings, strong community spirit, and excellent connectivity, Easton is an ideal choice for those seeking new builds near me or exploring new builds UK. Whether you’re a first-time buyer, a growing family, or an investor, Easton’s modern homes provide the perfect blend of comfort and convenience. Start your journey today and find your dream home in this charming village.


 English
English