EB1 Requirements Explained – Qualify for Your EB1
Nov 08, 2025The Best TikTok Video Download Tools for 2025:
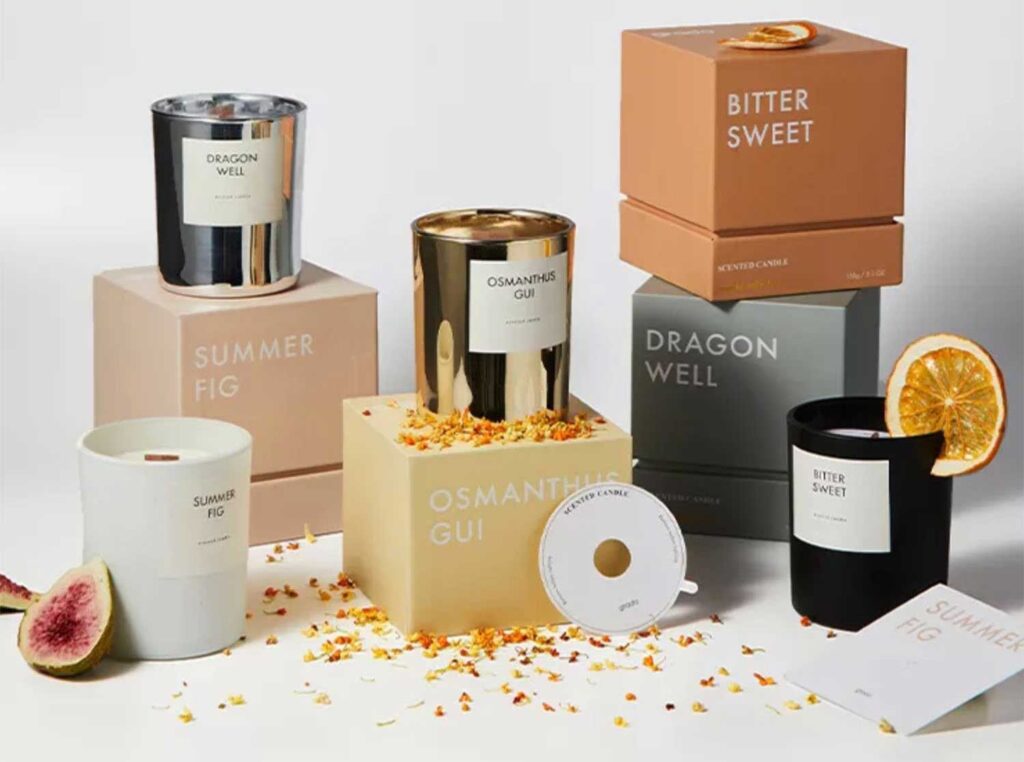
Nov 08, 2025Custom Die Cuts Boxes: The Ultimate Guide to
Nov 07, 2025Comparing Old City vs. Modern Living in Jerusalem
Nov 07, 2025Fire Guard Services in the USA | Protect
Nov 07, 2025Benefits of Hiring Licensed Security Guards in Los
Nov 06, 2025The Hidden Power of Local Backlinks for SEO
Nov 06, 2025MP3Juice vs. YTMP3: Which MP3 Downloader Wins?
Nov 06, 2025Rising Importance of Industrial Packaging in Chennai
Nov 06, 2025Rx Propellant’s 9 Lakh Sq. Ft. Lab Spaces
Nov 06, 2025How Private Security Prevents Crime in Urban Cities
Nov 05, 2025What Causes Bleeding Gums and How to Stop
Nov 05, 2025PowerPoint Template Guide for Stunning Presentations
Nov 05, 2025How Online Reviews Can Boost Your Brand Credibility
Nov 05, 2025Types of Banner Printing and Their Best Uses
Nov 05, 2025Birthday eCards for Him: The Perfect Way to
Nov 05, 2025Transform Your Bathroom with Perth Shower Screens &
Nov 04, 2025CMDA Approved Plots: What Chennai Buyers Should Know
Nov 04, 2025Key Traits of a Great Seasonal Agricultural Labor
Nov 04, 2025Power Creative Web Design Dubai with RedSpider Web
Nov 04, 2025Geek Bar Vape: A Deep Dive into Voyoria
Nov 03, 2025Elevate Your Brand with Expert Brand Logo Designing
Nov 03, 2025Denim Tears’ Approach to Sustainability
Nov 02, 2025Chrome Hearts Leather Goods Review
Nov 02, 2025Bold Logo Essentials Hoodies
Nov 02, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Online B.Com
Nov 01, 2025Why is ISI Mark Registration Mandatory for All
Oct 31, 2025What is Medical Summarization and Why Is It
Oct 31, 2025How to Choose the Best Video Editor for
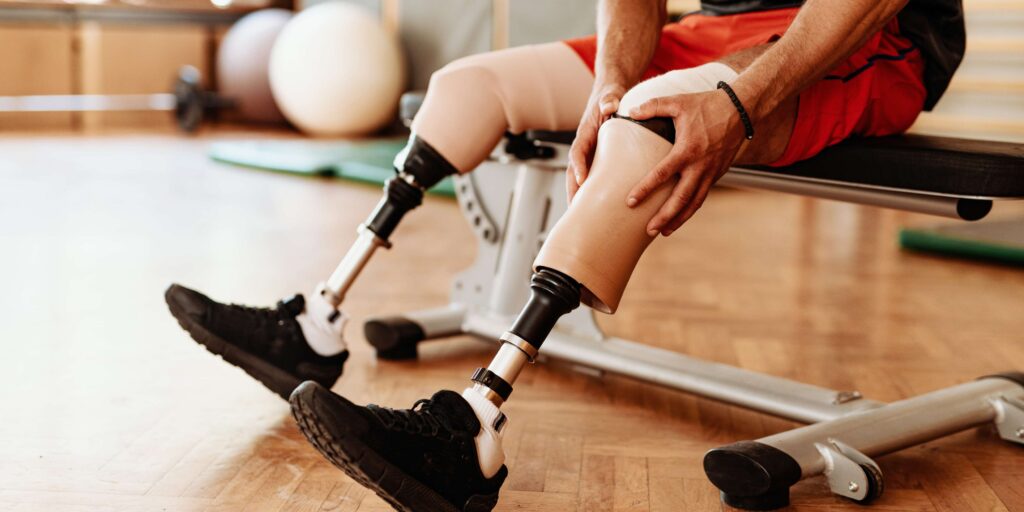
Oct 30, 2025What You Should Know Before Getting a Prosthetic
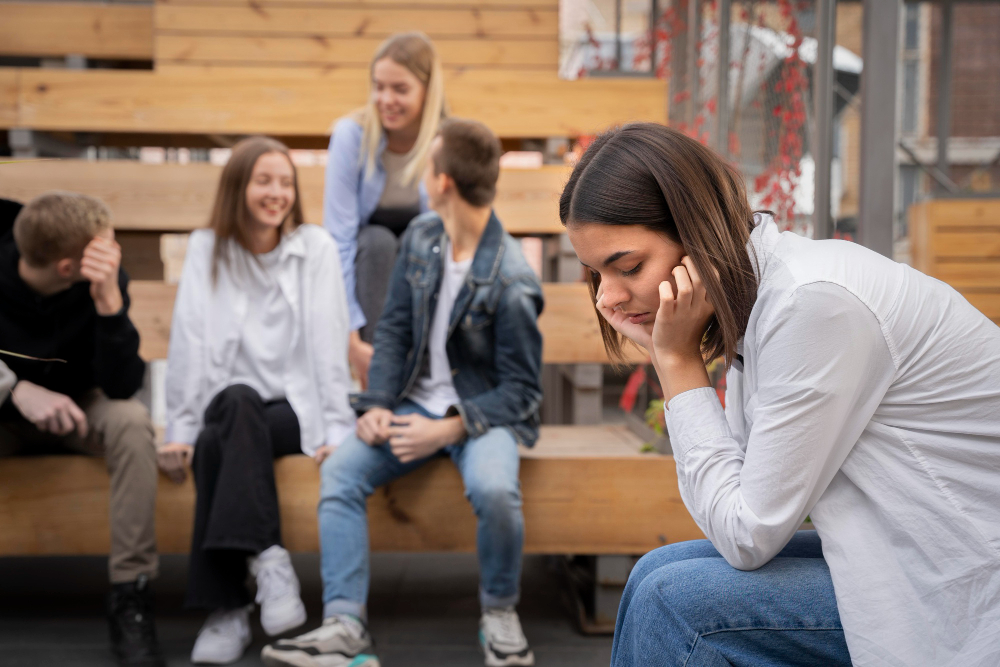
Oct 30, 2025The Mental Health Toll of Academic Deadlines and
Oct 30, 202512 Creative Employee Christmas Gifts to Mark a
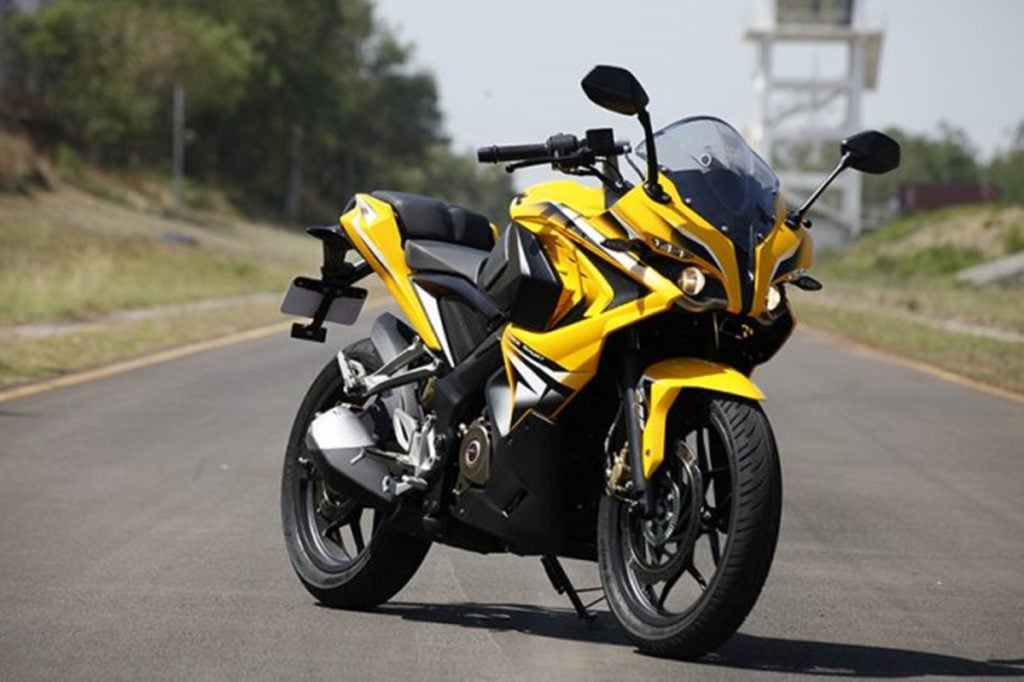
Oct 30, 2025Pulsar RS200 On-Road Price and Features – Is
Oct 30, 2025Small Kitchen? Here’s why an OTG Oven is
Oct 30, 2025Kilobytes Technologies: Elevating Startups in Mumbai
Oct 30, 2025The Best Uses for Personalized Stickers in Your
Oct 30, 2025The No-Stress Way to Clean Jets in a
Oct 30, 2025Custom Pillow Boxes for Distinctive Retail and Gift
Oct 30, 2025How to Send Money from Canada to Germany
Oct 29, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Home Nursing Services in
Oct 29, 2025Why SEBI Keeps Tweaking Futures and Options Rules
Oct 28, 2025Discover Chrome Hearts Germany – Premium Fashion and
Oct 28, 2025Tubidy MP3 Download Guide for Music Lovers
Oct 28, 2025Best Countries to Retire for Canadian Citizens in
Oct 28, 2025Best Study Visa Consultants in Delhi
Oct 28, 2025New York App Development Company Crafting Innovative
Oct 27, 2025Nav Grah Yantra: Aligning Planets with Inner Balance
Oct 27, 2025Discover Bold Urban Style with the Iconic Spider
Oct 27, 2025Tummy Tuck vs. Non-Surgical Options: Which Is Right
Oct 27, 2025Top Auto Paint Trends Redefining Car Style in
Oct 26, 2025Godrej Sora: The Epitome of Modern Luxury in
Oct 26, 2025A Smarter Future with Solar Energy with Battery
Oct 25, 2025The benefits of custom aluminum signs
Oct 24, 2025Send Christmas Gifts to USA Online: Unleash Festive
Oct 24, 2025Top European Countries to Retire on a Budget
Oct 23, 2025How Do Agencies Track and Prove Results in
Oct 23, 2025Why You Should Never Try to Handle Bail
Oct 23, 2025Emergency Eye Care in Etobicoke: When to Act
Oct 22, 2025Elevate Your Packaging Game with Custom Kraft Paper
Oct 22, 2025How to Pass a 4-Point Home Inspection
Oct 21, 2025What Ways Does PMP Certification Enhance Your Test
Oct 19, 2025Best Indoor Activities for Toddlers in Northridge
Oct 19, 2025Explore Mental & Emotional Benefits of Listen to
Oct 18, 2025Why Every Hotel Needs a Hospitality PR Company
Oct 17, 2025Boost Your Sales with an Effective PR Product
Oct 17, 2025How Product Launch PR Can Skyrocket Your Brand
Oct 17, 2025How a SaaS PR Agency Can Accelerate Your
Oct 17, 2025Top PR Companies for Startups Driving Media Success
Oct 17, 2025How PR Agencies Help Startups Win Investor and
Oct 17, 2025Top PR Strategies Every AI Company Should Use
Oct 17, 2025How AI is Transforming the Future of Public
Oct 17, 2025Hire Security for Event: Ensure Safety, Control, and
Oct 17, 2025How Can Skin Boosters Improve Your Skin Health
Oct 16, 2025Hire a Virtual Assistant for Social Media and
Oct 16, 2025How the AHA BLS Course Prepares You for
Oct 16, 2025How Can PPLI Life Insurance Transform Your Wealth
Oct 15, 2025Jobs in Dubai | Find Your Next Career
Oct 15, 2025Paying for Math Help vs. Paying Someone to
Oct 15, 2025How to Get the Best Score on Your
Oct 15, 2025Mobile App Development in Montreal: Trends and Best
Oct 15, 2025CPR Vs BLS: What’s the Difference and Which
Oct 15, 2025Cheap Property in Asturias Spain – Find Your
Oct 15, 2025YT5s: The Best Solution for High-Quality Video &
Oct 15, 2025A Complete Guide to the PADI Open Water
Oct 15, 2025Baby SIDS Monitor: Protecting Your Infant While You
Oct 14, 2025The Importance of Duct Cleaning in Laval for
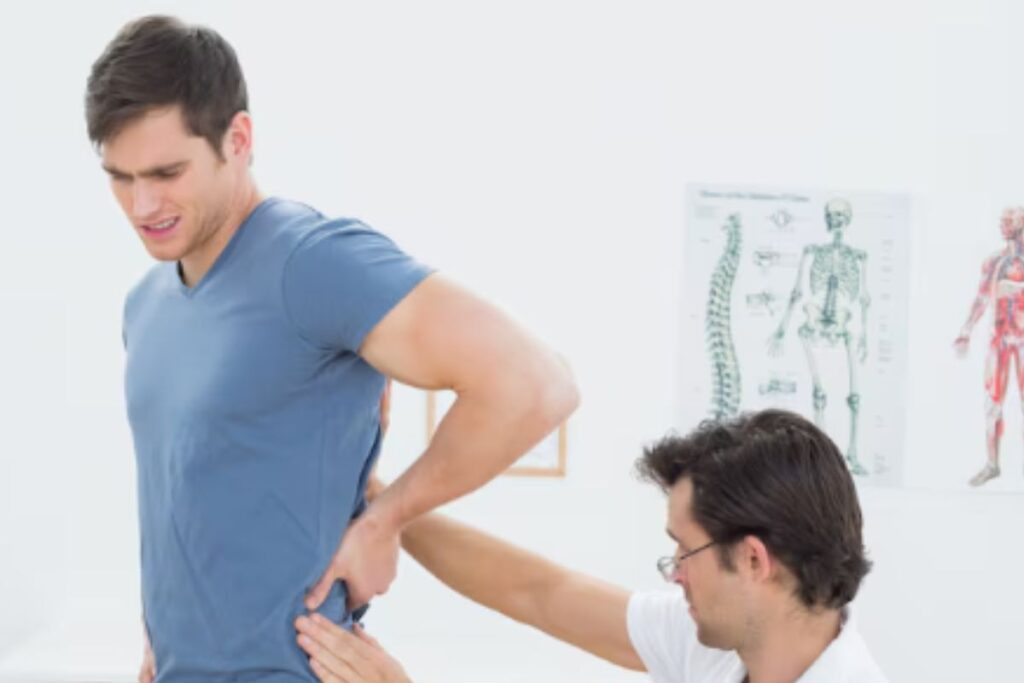
Oct 14, 2025Lower Back Pain Treatment: When to See a
Oct 14, 2025Before You Call a Bondsman: 7 Common Bail
Oct 14, 2025Payroll Software in India Solves its Challenges
Oct 14, 2025Best Web Design in Canberra – Hungry Bull
Oct 13, 2025SATV Online Live – Watch Latest Bangla News
Oct 13, 2025Luxury Hotels in Sylhet – Experience Elegance at
Oct 13, 2025Limited Edition Chrome Hearts Releases
Oct 12, 2025Trends in Warehousing & Logistics Real Estate
Oct 11, 2025Moonstone Energy: A Crystal for Balance and Clarity
Oct 11, 2025How to Build a Profitable Baby Products Shop
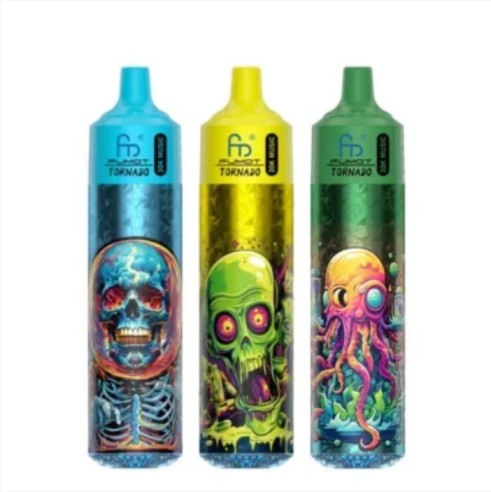
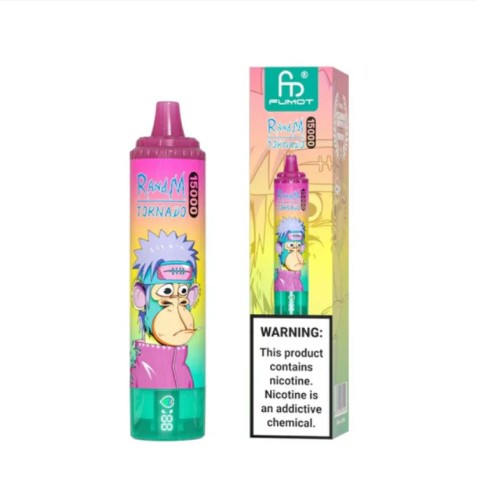
Oct 11, 2025R and M Tornado 30000 box of 10
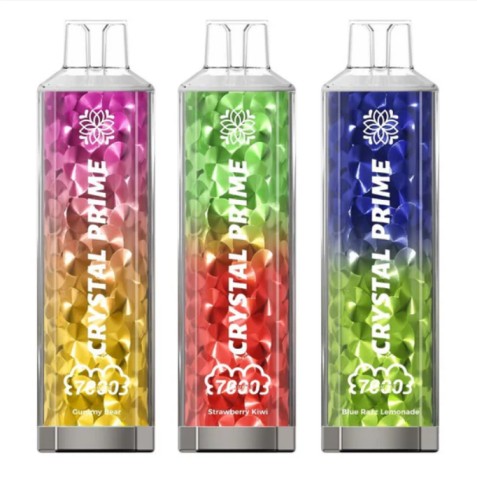
Oct 10, 2025Crystal Pro Max + 10000 Box of 10
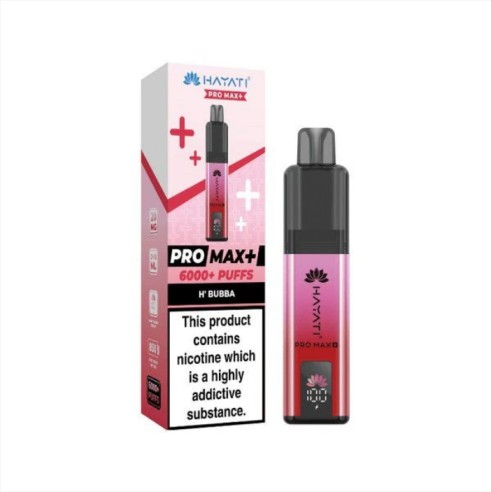
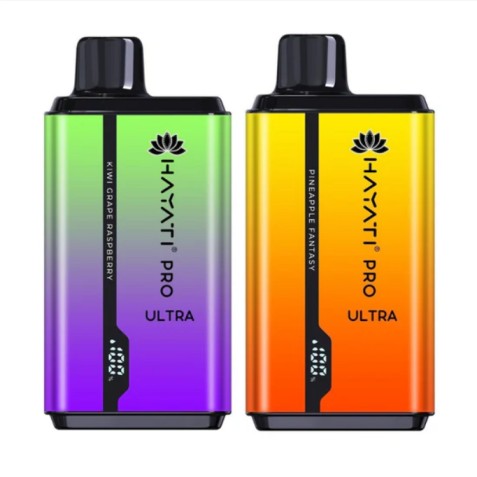
Oct 10, 2025Hayati Pro Max Plus 6000 box of 5
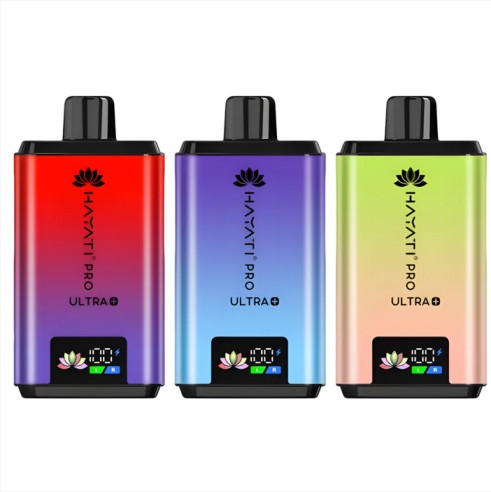
Oct 10, 2025Hayati Pro Ultra plus 25000 box of 5
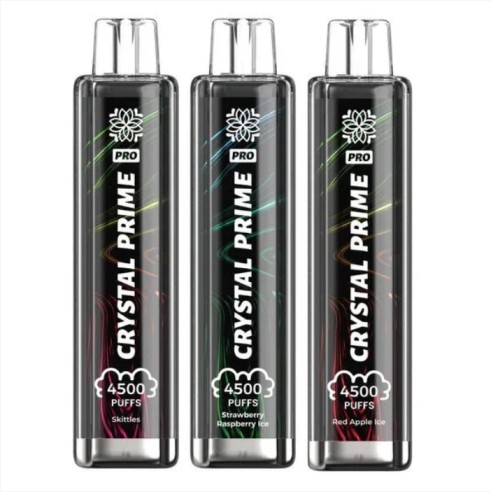
Oct 10, 2025Crystal Prime Pro 4500 box of 10
Oct 10, 2025Hayati pro Ultra 15000 box of 10
Oct 10, 2025Crystal Prime 7000 box of 10
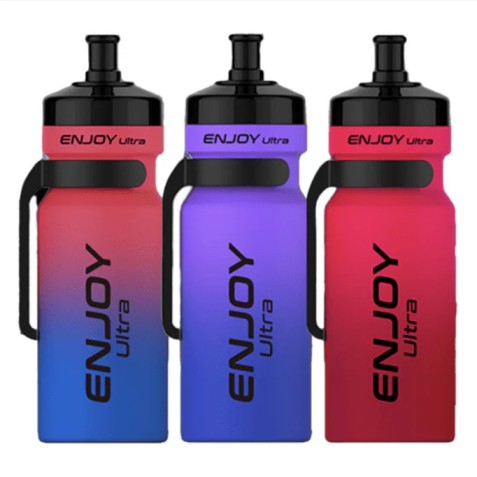
Oct 10, 2025Enjoy Ultra 9000 Puffs box of 10
Oct 10, 2025R and M Tornado 15000 box of 10
Oct 10, 2025R and M Tornado 9000 box of 10
Oct 10, 2025Hayati Pro Max 4000 Box of 10
Oct 10, 2025Crystal Prime Deluxe 18000 box of 10
Oct 10, 2025Custom Postcard Printing vs. Template Postcards
Oct 10, 2025What’s New in Ok Win Game 2025 Update
Oct 10, 20257 Essential Tips to Pick the Perfect Corner
Oct 10, 2025Plant Engineering Experts in Montana
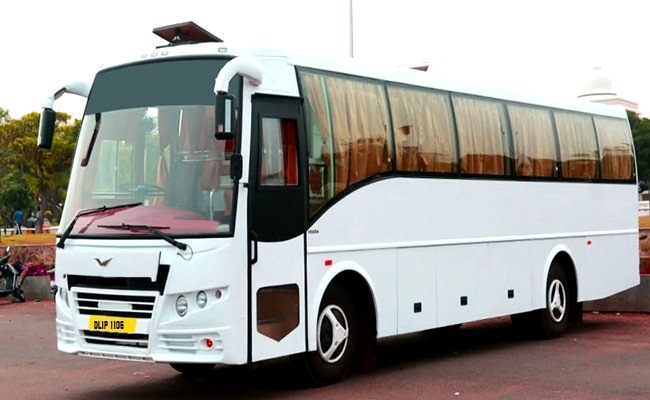
Oct 10, 2025Comfort, Safety & Ease of Travel with Coach
Oct 09, 2025What is the Difference Between Fire Bricks and
Oct 09, 2025How Pain Treatment Centers Use Technology for Better
Oct 09, 2025Shop Omada Cordless Grass Trimmers Now
Oct 09, 2025Ford Rental Dubai – Drive Style, Strength, and
Oct 08, 2025Learn How to Stay Consistent with Every Colour
Oct 08, 2025A Guide to Maid Services and Home Cleaning
Oct 08, 2025Discover the Best House Cleaning and Maid Services
Oct 08, 2025New Standard of Clean with House Cleaning Service
Oct 08, 2025Can You Avoid Airline Cancellation Fees on Cash
Oct 08, 2025Premium Delta & E-Cigarette Boxes – Redefine Luxury
Oct 08, 2025Cat Eye Bracelet – Protection, Clarity & Balance
Oct 07, 2025What Makes the 6 Club Worth Trying for
Oct 07, 2025Impact of Leavening Agents on Cake Texture
Oct 07, 2025Enterprise Application Development Company
Oct 07, 2025Tips to Organize your Schedule and Dispatch
Oct 07, 2025Empower Your Business with a Leading IT Solutions
Oct 06, 2025Tashan Game Free Recharge – Play, Win &
Oct 06, 2025How to Get a Virtual Office Address in
Oct 06, 2025Tattoo Pricing in Phuket with All the Details
Oct 06, 2025Bharat Club Colour Trading App – Win Real
Oct 06, 2025What Are Refractory PCPF Blocks and Where Can
Oct 04, 2025DLF The Magnolias Gurgaon – The Epitome of
Oct 03, 2025Teacher’s Guide to Top AI Checker Tools for
Oct 03, 2025Body Waxing for Sensitive Skin: Best Practices
Oct 03, 2025HR Software in India vs Traditional HR Methods:
Oct 03, 2025The Best DST File Converters for Smooth Results
Oct 03, 2025Celebrate Together: Festival Trips with a 50 Seat
Oct 02, 2025Party Bus Hire for Memorable City Journeys
Oct 02, 2025Why Halloween Candy Bracelets Are a Fun Gift
Oct 02, 2025Office Pantry Service for Workplaces
Oct 01, 2025Mahakoshal Refractory Fire Bricks in OMAN | Supplier
Oct 01, 2025Micro Market Vending Machines for Workplaces
Oct 01, 2025Best Fire Bricks in Ghaziabad | Manufacturer |
Oct 01, 2025The Art & Science Behind Perfect Baking
Oct 01, 2025Refractory Fire Bricks in Bhiwadi by BM Enterprises
Sep 30, 2025Which Business Card Design Works Best for You?
Sep 30, 2025Uratech Tool Carts and CNC Cabinets- Built for
Sep 30, 2025The Complete Guide to Digital Visiting Cards
Sep 30, 2025Professional Photography Services: Capturing Moments
Sep 29, 2025Lubricants Market to Witness Promising Growth
Sep 29, 2025How To Choose The Best Holographic Mylar Bags
Sep 29, 2025Fast Track Driving Licence: The Quickest Way to
Sep 29, 2025Face Serums in Lahore – Unlock Radiant Skin
Sep 29, 2025The 80/20 Rule: How the Pareto Principle Transforms
Sep 29, 2025Essentials Fear Of God Pullover Hoodie Black
Sep 27, 2025Flip or Decide: The Modern Way to Make
Sep 26, 2025Crystal Prime Deluxe 18000 Puffs Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025WGA Crystal 20000 Puffs Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025R and M 30000 Puffs box of 10
Sep 26, 2025Crystal Pro Max + 10000 Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025Crystal Prime Pro 4500 Puffs Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025WGA Crystal Pro Max 15000 puffs Box of
Sep 26, 2025Hayati Pro Ultra 15000 Puffs Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025Crystal Prime 7000 Puffs Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025Enjoy Ultra 9000 Puffs Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025R and M 15000 puffs box of 10
Sep 26, 2025R and M 9000 puffs box of 10
Sep 26, 2025What Makes the Best Wrap Around Soap Labels
Sep 26, 2025Hayati Pro Max 4000 Box of 10
Sep 26, 2025SIE Practice Questions: Tips and Strategies to Pass
Sep 26, 2025The Future of VR & AR in 3D
Sep 26, 2025Future of ONDO: ONDO Price Prediction and Investment
Sep 26, 2025Digital Growth Made Simple with DigiAtmos Solutions
Sep 26, 2025Blinds Installation White Plains NY – Transform Your
Sep 25, 2025Coach Hire UK with Routes to London
Sep 25, 202550 Seater Coach Hire for Stratford to Stansted
Sep 25, 2025What Can You Do About Modafinil at Buy
Sep 25, 2025The Best Option for Heathrow Travel: Coach Hire
Sep 25, 2025Side Gig to Main Job: Earn with AI
Sep 25, 202550 Seater Coach Hire Prices: Affordable Group Travel
Sep 24, 2025Exploring Comfort with UK Coach Hire for Long
Sep 24, 2025UK Coach Hire for Stress-Free Group Travel Across
Sep 24, 2025Hayati Pro Max Plus 6000 Puffs
Sep 24, 2025Preact vs React: Choosing Right JavaScript for Your
Sep 24, 2025How to Optimize Your Ecommerce Website for Organic
Sep 24, 2025How It Compares to Traditional Facials for Lasting
Sep 24, 2025Prepared Meals Delivered NJ: Tasty Nutrition at Your
Sep 23, 2025Start Your Group Adventure: 16 Seater Minibus Hire
Sep 23, 2025Simple Stock Analysis: 5 Steps to Find Profitable
Sep 23, 2025How to Minimize Wrinkles and Fine Lines on
Sep 23, 2025Guide to Infant Headband Bows: Style, Comfort, and
Sep 23, 2025Minibus Hire Walsall: Perfect for Day Trips &
Sep 23, 2025Types of Custom Outdoor Retail Signage
Sep 23, 2025Comfortable 7 Seater Taxi for Heathrow & Gatwick
Sep 23, 2025Blending Fun and Learning: How Online Phonics Makes
Sep 22, 2025Payroll Outsourcing: A Smarter Way to Manage Growth
Sep 22, 2025Shine India: Best place for Currency Solutions in
Sep 22, 2025Track IPO Subscriptions in Real-Time with These 7
Sep 22, 2025Trendy Unstitched Fabrics Frocks for Every Occasion
Sep 20, 2025How To Replace Defy Spare Parts For Lasting
Sep 20, 2025Custom Embroidery Patches and Quick Delivery Service
Sep 19, 2025Why Solar Energy with Battery Storage Is the
Sep 19, 2025Top-Rated Credit Conversion Experts in Okatie, SC
Sep 19, 2025The Sweetest Symbol of Love and Celebration
Sep 18, 2025Lanvin: Critiques of Scarcity in Merch
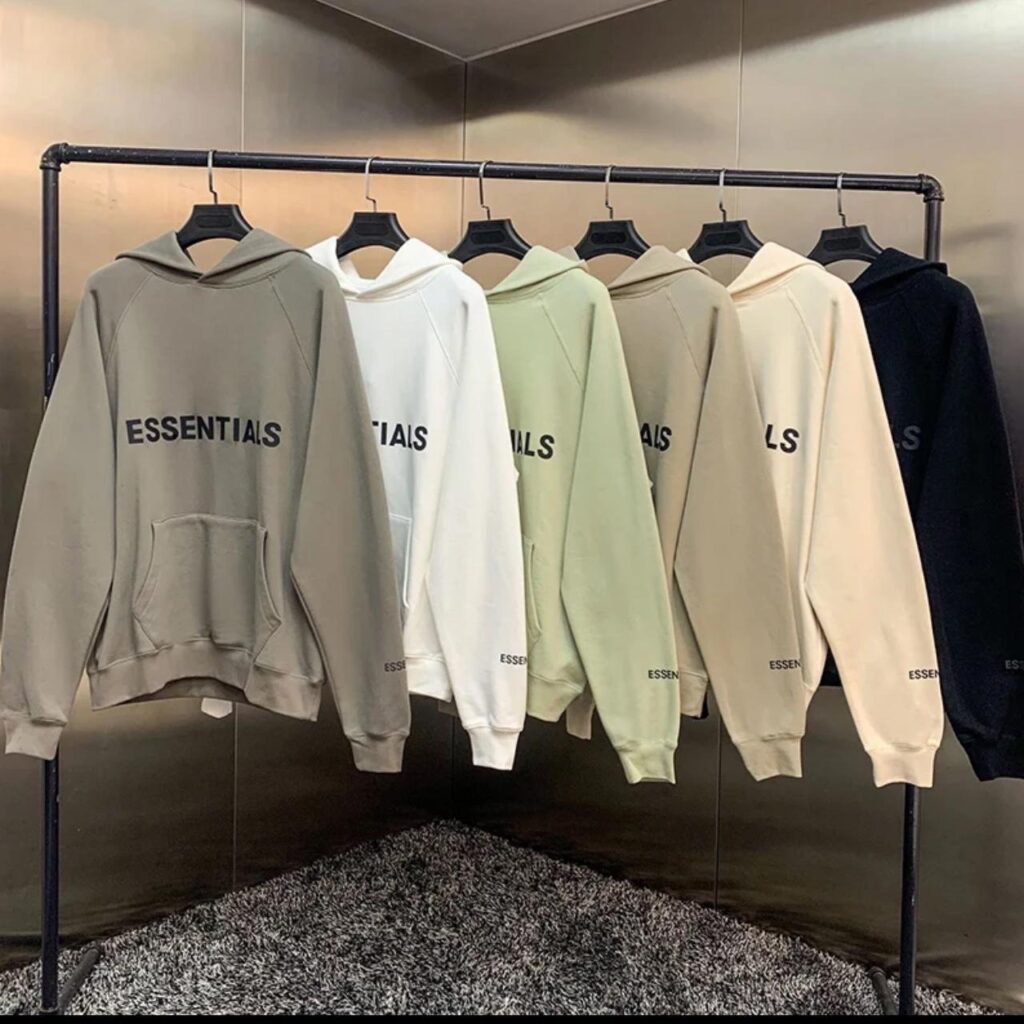
Sep 18, 2025High-Quality Essentials Hoodie for Daily Use
Sep 18, 2025“Best Way to Ship Car from Georgia to
Sep 18, 2025The Role of Panel Beaters in Restoring Structural
Sep 18, 2025Essentials Hoodie for Athleisure Outfits
Sep 17, 2025Essentials Hoodie Clean and Classic
Sep 17, 2025$uicideboy$ Merch That Doesn’t Sugarcoat Pain
Sep 17, 2025Your Adventure Look XPLR Merch
Sep 17, 2025$uicideboy$ Merch for Those Who Feel the Lyrics
Sep 17, 2025HydraFacial vs. Regular Facials – Which One Is
Sep 17, 2025Why Bakers Around the World Swear by Madagascar
Sep 17, 2025How to Save Money on London’s Premier Photography
Sep 17, 2025The Life of a Dozer: From Forest Clearing
Sep 17, 2025Central Park 104 – Redefining Luxury Living in
Sep 17, 2025Can Leather Kilts Replace Trousers in Men’s Everyday
Sep 17, 2025Best Gynecologist in Lucknow for Normal Delivery
Sep 16, 2025Dashing Guide to Choosing the Best Gift Boxes
Sep 16, 2025How Custom Brochure Printing Builds Brand Trust
Sep 16, 2025How Gold Trading Signals and XAUUSD Signals Help
Sep 16, 2025How to Apply for a British Passport:
Sep 16, 2025Expert Public Relations Tourism Services for 2025
Sep 15, 2025Expert SaaS Public Relations for Modern Tech Brands
Sep 15, 2025Top 10 Sig Sauer New Products Every Firearm
Sep 15, 20255 Effective TMJ Pain Relief Stretches for Gallup
Sep 15, 2025Dental Implants and Oral Hygiene: Best Practices for
Sep 15, 2025How to Manage Minor Orthodontic Issues at Home
Sep 15, 2025Can You Legally Use a Virtual Office for
Sep 15, 2025Choose the Best Digital Marketing Company for Your
Sep 15, 2025Opal and Tourmaline Meaning: The Dual Gems of
Sep 15, 2025History of Lederhosen: From Work Trousers to Cult
Sep 15, 2025Mastering ISO 13485 internal auditor training online
Sep 15, 2025How Can Custom Bath Bomb Boxes Improve Brand
Sep 15, 2025How Can Retailers Use Custom Cube Boxes Effectively?
Sep 15, 2025How Can Fast Food Boxes Boost Restaurant Branding?
Sep 15, 2025Greece Golden Visa Residency by Investment Program
Sep 15, 2025What Makes Rigid Candle Boxes Ideal for Luxury
Sep 15, 2025What Makes Cube Boxes Essential for Branding?
Sep 15, 2025How Can Custom Cigarette Boxes UK Improve Your
Sep 15, 2025The Role of Metal Fabrication in Modern Australia
Sep 15, 2025Can CCTV Cameras Be Jammed? Understanding Risks &
Sep 15, 2025Maximize Packaging Impact With Custom Pillow Boxes?
Sep 15, 2025How Can Custom Kraft Boxes Enhance Your Brand’s
Sep 15, 2025Benefits Do Small Businesses Get From Custom Printed
Sep 15, 2025Elevate Your Brand with Custom Beverage Packaging
Sep 15, 2025Durable Custom Bagel Boxes for Your Bakery
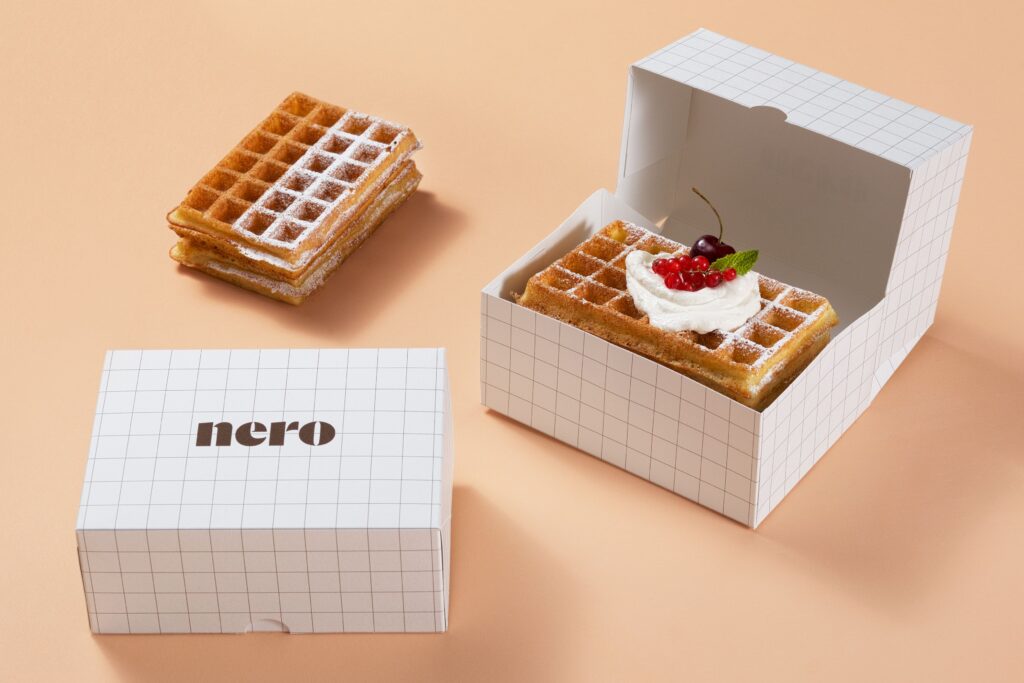
Sep 15, 2025Boost Sales with Custom Waffle Boxes
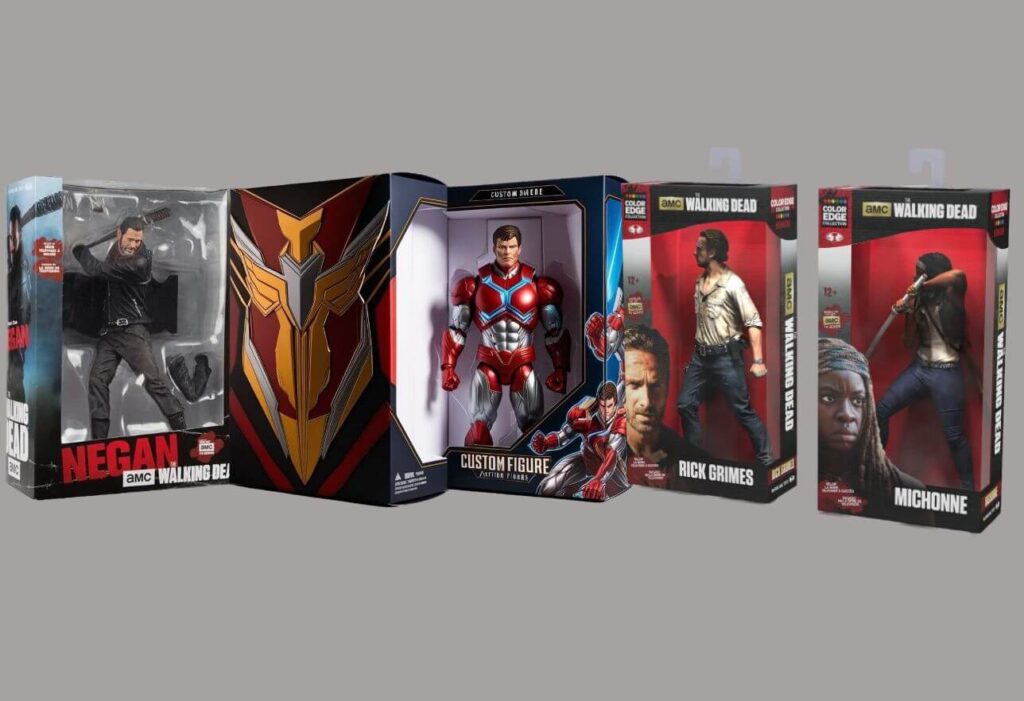
Sep 15, 2025Custom Action Figure Boxes Boost Toy Brand Marketing
Sep 15, 2025How to Optimize Layouts for Cheese Paper in
Sep 15, 2025How to Create Brand Visibility with Food Basket
Sep 15, 2025How Can Businesses Improve Layouts for Custom Food
Sep 15, 2025Civil Surveyor Course in Rawalpindi
Sep 15, 2025German Language Classes in Jaipur
Sep 14, 2025Essential Hoodie Your New Go-To
Sep 13, 2025Best Futures Prop Firms for Traders Looking to
Sep 13, 2025Best USB Flash Drive 2025 in New York
Sep 13, 2025Chrome Hearts Urban Street Hoodie
Sep 13, 2025AI Agents: Redefining the Future of Business
Sep 13, 2025Travis Scott Merch and Pink Palm Puff Guide
Sep 13, 2025How to Style Essentials Clothing for a Night
Sep 13, 2025Wearing Eric Emanuel Shorts With Always Do What
Sep 13, 2025Custom Packaging: A Powerful Tool for Modern Brands
Sep 12, 2025Buy Adderall in the USA at an Affordable
Sep 12, 2025Buy Adderall Online Next Day Shipping Available
Sep 12, 2025Buy Adderall Online with US Domestic Shipping
Sep 12, 2025Buy Adderall Online – Pay with Paypal
Sep 12, 2025Your Path to Fluency: The Premier German Language
Sep 12, 2025Celebrate in Style with Luxury Party Bus Hire
Sep 12, 2025Travel in Comfort with Modern UK Coach Fleet
Sep 12, 2025Your Definitive Guide: How to Import from China
Sep 12, 2025UK Coach Hire for Comfortable Birmingham to London
Sep 12, 2025See the World in Style: Discover Ray-Ban Sunglasses
Sep 12, 2025Group Adventures Made Simple with Minibus Hire Near
Sep 12, 2025Discover How Ratul Puri Is Helping India Reach
Sep 12, 2025How to Care for Moonstone: Protecting Its Delicate
Sep 12, 2025Why Soft Skills Matter More Than Ever in
Sep 12, 2025Crowns, Bridges, and Dentures in Sharjah: Care at
Sep 12, 2025Seeing the World in True Colors: Why Gray
Sep 12, 2025Cheap Coach Hire in the UK | Reliable
Sep 12, 2025How Many Calories in an Apple – Nutritional
Sep 12, 2025How AI is Revolutionizing HVAC Technology
Sep 12, 2025Best Lightweight Formal Wear for Hot Weather
Sep 11, 2025Affordable Handyman Services in Okatie You Can Trust
Sep 11, 2025Pre Wedding Photoshoot Outfits and Poses That Always
Sep 11, 2025Recycle Your Mobile Device: Get Top Value for
Sep 11, 2025Why White Label SMM Is a Strategic Edge
Sep 11, 2025Professional Teeth Whitening in Aldershot – Safe &
Sep 11, 2025Increase Leads with Proven SEO Services for Health
Sep 11, 2025Streetwear by Travis Scott and Pretty Little Thing
Sep 11, 2025Why You Should Choose Sliding Doors for Natural
Sep 11, 2025What Hidden Stories Lie Behind Every Cup of
Sep 11, 2025Roadstone vs Goodyear: Which Tyre Brand Wins?
Sep 11, 2025How to Choose Boudoir Photography Virginia Beach and
Sep 11, 2025How to Style Your Home Like a Pro
Sep 11, 2025SEO In the Era of AI: Emerging as
Sep 10, 2025Morris Town Limo Chauffeur Driven Car Hire
Sep 10, 2025VIP Travel Experience with Black Swan Chauffeurs
Sep 10, 2025How to Choose the Best Graphics Designing Company
Sep 10, 2025How to Find the Perfect Expert for Your
Sep 10, 2025From Stussy Hoodies to Broken Planet Market: Inside
Sep 10, 2025What is Custom Plasma Cutting and Its Role
Sep 10, 2025How to Balance Work and Study to Advance
Sep 10, 2025Luxury Apartments in Lucknow – A New Standard
Sep 10, 2025We Buy Houses in Georgetown Fast – Get
Sep 10, 2025Car Rental at CLT Your Guide to Travel
Sep 10, 2025Cash House Buyers in Boulder City: Sell Your
Sep 09, 2025Carpets in Dubai: Elevate Your Home with Luxurious
Sep 09, 2025We Buy Houses In Milton Florida – Sell
Sep 09, 2025How to Choose the Best Plumber in Golden
Sep 09, 2025Car Service to Raleigh NC Airport | Affordable,
Sep 09, 2025What to Expect When Ordering Custom Printed Yard
Sep 08, 2025Winter Fashion Redefined with High Neck Sweaters for
Sep 08, 2025The Advanced Vaporesso Luxe Q2 SE for Ultimate
Sep 05, 2025Floor Plans Designed for Comfort and Modern Living
Sep 05, 2025Why 2026 Could Be the Best Year to
Sep 04, 20255 Key Tools for Quality Control and Assurance
Sep 03, 2025JetBlue Airlines Flight Change Policy: A Guide To
Sep 03, 2025Properties on Ayodhya Road Lucknow – A Modern
Sep 03, 2025Fast Business Loans: A Quick Solution for Growing
Sep 02, 2025Overcoming Sales in the Hybrid Era: New Tactics
Sep 02, 2025Master Forex Skills with a Trading Demo Account
Sep 01, 2025Site Plan Overview for Comfortable and Modern Living
Sep 01, 2025How Wooden Pallets Are Used in the Transport
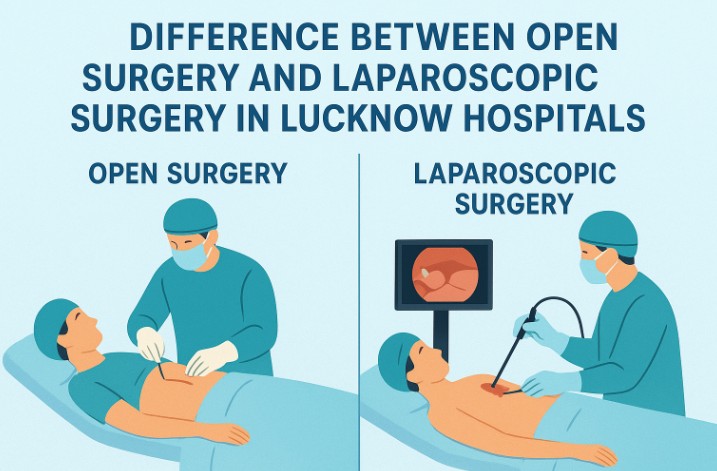
Aug 30, 2025Types of Plastic Surgery in Lucknow: Cosmetic vs.
Aug 29, 2025Couples Therapy Near Me: How Local Experts Help
Aug 29, 2025What SEO Services Do Agencies Typically Offer?
Aug 29, 2025Brand Logo Designing and Logo Digitizing Services
Aug 29, 2025Top Website Design Trends to Watch in 2025
Aug 28, 2025Smart Cash Handling: Organize with a Locked Money
Aug 28, 2025Why Should You Call a Locksmith in Pimlico
Aug 28, 2025How Cloud Services Drive Innovation in Startups
Aug 27, 2025Vintage Car Rental in Jaipur – Royal Cars
Aug 26, 2025Find the Best Kids Photography Near Me –
Aug 25, 20255 Ways Cloud Services Help Startups Compete with
Aug 21, 20253 Best MOD APK Games That Make Every
Aug 21, 2025Expert Painters and Basement Remodeling in Cambridge
Aug 21, 2025Why You Need a Criminal Immigration Lawyer:
Aug 20, 2025Transportation and Logistics Management Solutions
Aug 20, 2025Best SEO Services in Delhi: How Local Agencies
Aug 20, 2025Top 8 Places to Visit in Puri
Aug 18, 20255 Common Myths About Home Window Tinting Louisville
Aug 18, 2025Popular Places to Visit During Adi Kailash Yatra
Aug 18, 2025Why Pakistani Wedding Dresses at Rang Jah Trending
Aug 16, 2025How to Apply a Wig Perfectly: Complete Guide
Aug 16, 2025Couples Dance Lessons and Wedding Dance Classes:
Aug 15, 2025Plan Romantic Xitang Tours with Your Way Holiday
Aug 13, 2025Best Banquet Halls with Top Catering Services
Aug 12, 2025Leyla Alaton Biography – Inspiring Life, Career &
Aug 12, 2025Is Hair Transplant in Pakistan Worth It? A
Aug 12, 2025Ivermectin Iverheal 12 mg – Uses, Benefits, Dosage,
Aug 12, 2025Where to Find Scenic Homestay in Sonmarg?
Aug 11, 2025Minimalist Look, Maximum Comfort – Essential Hoodie
Aug 09, 2025Electric Fireplaces: The Perfect Blend of Style and
Aug 09, 2025Cloud Storage: The Future of Data Management in
Aug 09, 2025The Perfect Blend of Durability and Style
Aug 08, 2025The Benefits of Using Cat5e CMP in Commercial
Aug 08, 2025Boost Your Child’s Success with Online English and
Aug 08, 2025VMware Horizon Cloud License Supplier in India
Aug 08, 2025How Custom Wood Hoods Add Character to Any
Aug 07, 2025Shop All Men’s Footwear Without Regret: A Zero-Fluff
Aug 07, 2025Damac Lagoons Property for Sale | Waterfront Homes
Aug 07, 2025Why Hiring a PPC Expert Can Skyrocket Your
Aug 07, 2025What to Look for When Buying a Basketball
Aug 07, 2025Why Hiring an AdWords PPC Consultant Boosts Your
Aug 07, 2025Top Reasons to Invest in Dubai Real Estate
Aug 07, 2025What Are the Benefits of Working with a
Aug 07, 2025Need Taxis to Heathrow Near Me? Here’s What
Aug 07, 2025What is the Best Tour Group for Iceland?
Aug 07, 2025Why Hair Transplant in Pakistan Is Gaining Global
Aug 07, 2025Elementor #22458
Aug 07, 2025How AdsDiary Became the Best SEO Company in
Aug 07, 2025Stämning dolda fel: Din kompletta juridiska guide
Aug 07, 2025Why Brides Love Pakistani Mehndi Dresses at Rang
Aug 07, 2025Where Junior Jewels Shirt Become Pop Culture Icons
Aug 07, 2025Golden Visa for Real Estate Investors Guide to
Aug 07, 2025Corteiz Streetwear Essentials: How to Build a Trendy
Aug 06, 2025A Precision Solution for Modern Industrial Demands
Aug 05, 2025How Beewel Ensures the Purity of Every Drop
Aug 02, 2025QuickBooks Error 15276 | Payroll File In Use
Jul 30, 2025Chic and Modern Rings for Girls at WearItWell.pk
Jul 30, 2025The Critical Role of Event Medical Services in
Jul 30, 2025Are You Experiencing Varicocele Grade 4 Symptoms?
Jul 30, 2025White Label SEO Reseller Company to Help You
Jul 30, 2025Smart Use of MyMathLab Answers to Succeed in
Jul 28, 2025North Miami Car Accident Lawyer – The Perazzo
Jul 28, 2025Top Reasons to Use a Certified NAATI Translator
Jul 28, 2025Why a NAATI Translator Is Key to Trusted
Jul 26, 2025The Value of CNC Machining in Modern Precision
Jul 26, 2025Next-Gen Fashion 2025: The Power of Accessories
Jul 26, 2025Volleyball Net Height Guide: Rules, Sizes & Pro
Jul 26, 2025What To Know Before Getting Spray Foam Insulation
Jul 24, 2025Upgrade Your Basement with Durable and Stylish Floor
Jul 23, 2025Drift Hunters and the Rise of Browser-Based Racing
Jul 23, 2025Dordle: A Double Dose of Word Puzzle Fun
Jul 23, 2025Best Forex Trading Platforms | Tradewill
Jul 23, 2025Fai tornare il tuo PC come nuovo con
Jul 22, 2025Evan Bass Men’s Clinic Discusses the Importance of
May 21, 2025Charles Spinelli Unlocks the Secrets of Designing a
May 19, 2025What to Expect from a Financial Advisor in
May 17, 2025Steven Rindner On Impact of Weather Conditions in
May 15, 2025Is Post-Op IV Ozone Therapy Useful for Joint
May 03, 2025How Do You Take Care of Your Vehicle
May 03, 2025Does Oxygen Facial Reduce Large Pores Too?
May 03, 2025Discover the Bold Streetwear Power of the Iconic
May 03, 2025Choose VIP Travel Agency for Luxury Adventures
May 02, 2025Why Choose HydraFacial for Flawless Skin in Dubai?
May 02, 2025Bitachon for Beginners: A Quick Guide
May 02, 2025Top Skin Whitening Treatments in Dubai: A Quick
May 02, 2025Download GB WhatsApp APK – Updated Version (2025)
May 02, 2025Top Guma – Affordable Tires for Every Car,
May 02, 2025Top Guma – Wide Selection of Car Tires
May 02, 2025GV GALLERY® || Raspberry Hills Clothing Store ||
May 02, 2025How Does Wegovy Injections Compare to Saxenda?
May 02, 2025Resume writing services – hirex
May 02, 2025Finding the Best Naperville Fence Company for Your
May 02, 2025Unlock the Power of Numbers with a Numerology
May 02, 2025Title: Top Online Game Genres to Watch in
May 02, 2025Who Is the Biggest Enemy of Lord Vishnu
May 02, 2025Reliable Manchester to Airport Taxi Service – Fixed
May 02, 2025Complete Greenhouse Solutions by EKO TEPLYTSIA Kyiv
May 02, 2025How Henceforth Leads as a Premier App Development
May 02, 2025High-Quality Jewellery Design CAD Files Online
May 02, 2025Tassie-Tough MTA: Where Stability Meets Progress
May 02, 2025The Ultimate Guide to ISO Training: Top Management
May 02, 2025Crafting Cute and Creative Party Decor for Every
May 01, 2025Halal Certification: What It Is and Why It’s
May 01, 2025How Professional CIPD Help Can Boost Your Academic
May 01, 2025Choosing the Right Retirement Homes in Sydney: A
May 01, 2025Drive in Style with Premium Android Car Radios
May 01, 20256+ Years of Quality Android Car Stereo Installations
May 01, 2025Reliable Romiley to Manchester Airport Taxi Service
May 01, 2025United States Semiconductor Market Size & Share |
May 01, 2025Masters in Ireland for Indian Students: Best IT
May 01, 2025One Goal. One Result. The Best CUET Coaching
May 01, 2025Top Castles and Palaces to Visit in Hungary
May 01, 2025How to Choose the Best PPC Management Company
May 01, 2025Living Room Design Tips from a Knoxville Remodeling
May 01, 2025Are One-Size-Fits-All Marketing Services Worth It?
May 01, 2025Badson US || Official Badson Clothing Store ||
Apr 30, 2025Bajaj Pulsar NS 160: The Perfect Bike for
Apr 30, 2025محل عطور فاخر يقدم أجود الروائح وتجربة تسوق
Apr 30, 2025The Timeless Allure of Agarwood Oud
Apr 30, 2025Hire Laravel developer at affordable price
Apr 30, 2025Is ClearLift Laser Suitable for Mature Skin?
Apr 30, 2025Is PDO Mono Threads Right for Your Skin?
Apr 30, 2025ISO 45001 Training: Essential Steps for a Safer
Apr 30, 2025Trusted Mobile Notary in Pasadena – Fast &
Apr 30, 2025Proven Facts to Fix QuickBooks Error Code 15276
Apr 30, 202510 Compelling Reasons to Buy Space Binoculars
Apr 30, 2025Why Are i7 Laptops Still the Top Pick
Apr 30, 2025What Is Rhinoplasty and How Does It Work?
Apr 30, 2025Unlocking Pharma Success with Real World Data in
Apr 29, 2025Top SEO Services in Los Angeles: Boost Your
Apr 29, 2025Does ClearLift Laser Work on Acne Scars?
Apr 29, 2025Is Hair Transplant Effective for Balding Men?
Apr 29, 2025Insurance Company in Abu Dhabi – Tailored Solutions
Apr 29, 2025GB WhatsApp APK Download 2025 (Latest Version)
Apr 29, 2025Is Fat Injections Better Than Fillers for Facial
Apr 29, 2025Reliable Taxi from Stockport to Manchester Airport
Apr 29, 2025Luxury Sprinter Van Limo Service – Comfort, Style
Apr 29, 2025Our Uniting Classic USA Craft with Chrome Heart
Apr 29, 2025How a Web Development Company Builds Websites That
Apr 29, 2025How a Moisture Analyzer Improves Product Quality
Apr 29, 2025Reporting CSRD : Automatisez vos processus
Apr 29, 2025Top 10 Features to Look for in a
Apr 29, 2025Top Platforms to Sell Google Play Gift Card
Apr 29, 2025Dust Collector Manufacturer in India
Apr 29, 2025Pharmacovigilance in New Zealand – DDReg Pharma
Apr 29, 2025The #1 Natural Snoring Solution — NiteHush Pro
Apr 29, 2025Understanding Mental Health: A Beginner’s Guide
Apr 29, 2025How to Choose Perfume Based on Personality?
Apr 29, 2025Pharma Commercial Analytics and Consulting in 2025
Apr 29, 2025Best Airport Limo Service – Comfort, Luxury, and
Apr 29, 2025Fast Car Battery Replacement in Abu Dhabi –
Apr 29, 2025Mobile Tyre Repair in Abu Dhabi: 24/7 Roadside
Apr 29, 2025Complete Guide to Car Towing Services : 24/7
Apr 28, 2025Why Companies Need a Better Strategy for a
Apr 28, 2025Top Features to Look for When Developing Book
Apr 28, 2025Southampton Limo Service | Luxury Car & Airport
Apr 28, 2025Black Leather Coat for Women for Effortless Winter
Apr 28, 2025Top 7 Secrets to Extend Your Car AC
Apr 28, 2025Taxi from Glasgow to Manchester Airport | Affordable
Apr 28, 2025Kundali Houses Explained: Your Horoscope Secrets
Apr 28, 2025Top 10 Business Schools in Jaipur You Shouldn’t
Apr 28, 2025Why Invest in Property in Sector 10 &
Apr 28, 2025How to Choose the Right Solar Battery for
Apr 28, 2025Is Freckles and Blemishes Treatment Permanent?
Apr 28, 2025Unique Themes for Adelaide Wedding Receptions
Apr 28, 2025How to Grow Your Instagram Followers: A Strategic
Apr 28, 2025Book Trusted Newark Airport Limo Services | Noor
Apr 27, 2025GB WhatsApp APK (2025) – Latest Version Download
Apr 27, 2025Badson US || Official Badson Clothing Store ||
Apr 27, 2025Why Corteiz Hoodie is Perfect for Everyone
Apr 26, 2025Does Orlebar Brown Clothing Provide Fabric of the
Apr 26, 2025The Loverboy Hat: A Revolutionary Symbol in the
Apr 26, 2025In Glock We Trust Shirt has the most
Apr 26, 2025Why Sp5der Hoodie Is The Best Accessory You
Apr 26, 2025The Emergence of Hellstar Clothing in the Fashion
Apr 26, 2025Serenede jeans– Top Quality Brand
Apr 26, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Swiss Oud
Apr 26, 2025Top 8 Hayati Pro Max 6000 Flavours that
Apr 26, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Premium Oud
Apr 26, 2025Les meilleures saveurs de vapotage de Ghost Pro
Apr 26, 2025Complete Information on Original Oud Attar and Its
Apr 26, 2025De beste vaping smaken van Ghost Pro 3500
Apr 26, 2025Everything You Need to Know About White Oud
Apr 26, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Deer Musk,
Apr 26, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Oud Hindi:
Apr 26, 2025Unlock Your Week: Aquarius Weekly Horoscope Guide
Apr 26, 2025Does Acne Scar Treatment Lighten Dark Marks?
Apr 26, 2025Affordable Gastric Bypass Surgery for Weight Loss in
Apr 25, 2025The Pros and Cons of Static Site Generators
Apr 25, 2025Affordable Men’s Fashion: Best Stores to Shop
Apr 25, 2025Boost Your BPO Performance with Smart CRM Software
Apr 25, 2025How to Raise Emotionally Strong Kids as a
Apr 25, 2025Gallery Dept T-Shirt: Streetwear
Apr 25, 2025How to Make Your Hair Look Shiny and
Apr 25, 2025Is Your Hampshire Website Mobile-Friendly?
Apr 25, 2025Top 10 Electrical Companies in Dubai
Apr 25, 2025Unlock the Web with CroxyProxy – The Ultimate
Apr 25, 2025What are the common mistakes that you have
Apr 25, 2025How to Maintain Non-Surgical Hair Replacement?
Apr 25, 2025The Benefits of Hiring a Local Canberra Wedding
Apr 25, 2025Need a Blocked Sink Fix in Stourbridge? Contact
Apr 25, 2025Boost Your Business with Local SEO Services in
Apr 24, 2025San Diego SEO Services for Higher Rankings &
Apr 24, 2025Real Estate App Development: Essential to Build a
Apr 24, 2025Empyre | Empyre Jeans & Pants | Official
Apr 24, 2025The Rise of Natural Skin Care: Is Makeup
Apr 24, 2025Level Up Your Irrigation Game with These Top-Rated
Apr 24, 2025Soil Pipe Blocked Again? Here’s How to Solve
Apr 24, 2025Struggles Faced by New Moms & Tips to
Apr 24, 2025The Best Passive Real Estate Investment Options in
Apr 24, 2025The Pros and Cons of Investing in Custom
Apr 24, 2025Website Design Pitfalls for Small Businesses: How to
Apr 24, 2025The Role of SEO Tools in a Data-Driven
Apr 24, 2025Choosing the Right Electrician in Adelaide
Apr 24, 2025How Retargeting Can Drive Conversions and Boost ROI
Apr 24, 2025How to Choose the Right Disability Support Provider
Apr 24, 2025Private Taxi from London to Manchester Airport –
Apr 24, 2025How Technology is Changing the Path of Marriage
Apr 24, 2025Mukhyamantri Kisan Kalyan Yojana
Apr 24, 2025Is Organic Pumpkin Peel Better Than Chemical Peels?
Apr 24, 2025Building Smart Chatbots with PHP for Better UX
Apr 24, 2025Professional Help With Writing Thesis for Students
Apr 24, 2025The Kashyap Samhita and the Role of CSS
Apr 24, 2025NYC Cleaning & Maintenance – Trusted Experts for
Apr 23, 2025The Ultimate Guide to : A Luxurious Travel
Apr 23, 2025Realme 2025 Vision: AI Smartphones, & What’s Next
Apr 23, 2025How to Save Money on Car AC Repairs:
Apr 23, 2025Elevating Hygiene Standards in Every Space
Apr 23, 2025Top Certifications Pursue Alongside Your MS in Data
Apr 23, 2025Why Gold Bracelets Are a Must-Have in Every
Apr 23, 2025Smart Property Management Across the New York Metro
Apr 23, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Tummy Tuck
Apr 23, 2025Leo Daily Horoscope – Your Complete Guide
Apr 23, 2025Why Sure Shade Is the Leading External Venetian
Apr 23, 2025The Truth About Finding a Limo Service That’s
Apr 23, 2025Top Benefits of Virtual Office Valdosta GA for
Apr 23, 2025Your Guide to Luxury and Reliability in Northern
Apr 23, 2025UnitConnect: Simplify Commercial Property Management
Apr 23, 2025Smarter Real Estate Tools with UnitConnect Software
Apr 23, 2025How to Safely Overclock with the Intel Overclocking
Apr 23, 2025What Interest Rate Hikes Really Mean for Stock
Apr 23, 2025The Powerful Ruby: Discover the Top Ruby Gemstone
Apr 23, 2025Affordable Taxi from London to Manchester Airport
Apr 23, 2025Unlocking the Secrets of the Triangle in Palmistry
Apr 23, 2025Best IT Services in Oakland for Startups &
Apr 23, 2025How do I speak to someone at Breeze?
Apr 23, 2025How do I talk to a real person
Apr 23, 2025Buy Get Well Soon Flower Online for Her
Apr 23, 2025California Needs Drivers: Apply Now for the Best
Apr 23, 2025Botox Isn’t Just for Women: Men Embrace a
Apr 23, 2025Master Tableau with Expert Tableau Assignment Help
Apr 23, 2025The Rise of Cortiez Cargos: A Streetwear Staple
Apr 23, 2025Essentials Shorts: The Perfect Blend of Comfort and
Apr 22, 2025Why Choosing a Content Writing Agency in Houston:
Apr 22, 2025How to Use Your Intuition to Create Magnetic
Apr 22, 2025Mastering Evidence-Based Practice in NURS-FPX 4030
Apr 22, 2025Is Male Hair Loss Fixed by Best Trichologists?
Apr 22, 2025Food Safety Leader: FSSC 22000 Lead Auditor Course
Apr 22, 2025Top 10 Things to Know Before Visiting Maine
Apr 22, 2025Top Benefits of Installing Sliding Glass Doors in
Apr 22, 2025Book Trailer Services: A Smart Way to Promote
Apr 22, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Buying a
Apr 22, 2025Trusted Experts for Quality Cleveland Roof Repairs
Apr 22, 2025ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Training in Bangalore
Apr 22, 2025Broken Promises and the Healing Power of God
Apr 22, 2025How to Choose the Best Body Spa in
Apr 22, 2025Originalteile und Nachbauteile bei ORAP GMBH
Apr 22, 2025Original- und Nachbauteile direkt vom Fachhändler
Apr 22, 2025Ihr Partner für hochwertige Autoteile im Groß- und
Apr 22, 2025Get Your Towbar Fitted by Experts in Bishop’s
Apr 22, 2025How Body Pillow Shapes Affect Your Spine, Joints,
Apr 22, 2025The Role of Solar Power in Sustaining Military
Apr 22, 2025Which Areas in Dubai Have the Most Promising
Apr 22, 2025Why ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Training Could Be
Apr 22, 2025Discover New Builds in Easton: Modern Living
Apr 22, 2025Tips to choose the best kids backpack
Apr 22, 2025How Is G Cell Treatment Different From PRP?
Apr 22, 2025Which Football League Offers the Best Tactical Depth
Apr 22, 2025Is Renting or Buying a Home Better for
Apr 22, 2025A Smarter Way to Trade Stocks, Forex, and
Apr 22, 2025Graceful Church Suits Every Woman Should Own
Apr 22, 2025Recruitment agency in delhi- hirex
Apr 22, 2025Badson US || Official Badson Clothing Store ||
Apr 22, 2025Corteiz Clothing UK RTW Official Store | Cortiez
Apr 21, 2025Explore Livingston Park and Cabin Rentals in Texas
Apr 21, 2025Best Peking Duck and Curry Crab in Houston
Apr 21, 2025Finding the Right Pet Veterinary Clinic in Qatar
Apr 21, 2025Maximize Space and Style with Stackable and Metal
Apr 21, 2025Embrace the East with Every Sushi Roll at
Apr 21, 2025Sushi Point: Discover the True Spirit of Sushi
Apr 21, 2025Authentic Eastern Flavors, Perfected at Sushi Point
Apr 21, 2025How Do i5 and i7 Processors Compare for
Apr 21, 2025Samsung A26 Price in Pakistan – Specs You
Apr 21, 2025Technical SEO Done Right: Tips from a San
Apr 21, 2025Affordable SEO Services: A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 21, 2025Does Fat Injections Help Sculpt the Body?
Apr 21, 2025MBA in HR Management in Jaipur: Classroom to
Apr 21, 2025Everything You Need to Know About Liposuction in
Apr 21, 2025Find out what colleges in Jaipur offer mechanical
Apr 21, 2025Private Taxi from Blackpool to Manchester Airport –
Apr 21, 2025Intel HD Graphics vs. Dedicated GPUs: What’s Better?
Apr 21, 2025StrikeIT: Trusted SEO Company in Lucknow
Apr 21, 2025Why Split & Multi-Split ACs Suit Homes and
Apr 21, 2025Does Botox for Sweaty Gland Block All Sweat?
Apr 21, 2025Best Custom Patches in Malaysia
Apr 21, 20255 Important Health Benefits Of The Shecup Silicone
Apr 21, 2025Part-Time Jobs in Germany for International Students
Apr 21, 2025Affordable Taxi from Blackpool to Manchester Airport
Apr 20, 202570 Inch Bed Frame Maintenance Tips: to Keep
Apr 19, 2025The Beauty of Handmade Shell Jewellery
Apr 19, 2025Exotic Ride Rent A Car in Dubai
Apr 19, 2025WordPress Experts for High-Converting Sites
Apr 19, 2025Key Benefits of Combining Your MOT Test and
Apr 19, 2025Best gold buyers |Sell gold for cash |Hindustan
Apr 19, 2025Statistics Assignment Help – Expert Stats Solutions
Apr 18, 2025Mertra Clothing || Sale Up To 40% Off
Apr 18, 2025Rhinoplasty Cost in Lahore Explained: Find the Right
Apr 18, 2025E-Commerce and Q-Commerce: Compare all Details
Apr 18, 2025Ukraine Premier Vascular Center – Discover AngioLife
Apr 18, 2025Trusted Vascular Solutions in Ukraine
Apr 18, 2025Best Ethernet Cable for Gaming: A Perfect Guide
Apr 18, 2025Sector 140A Noida: A Prime Location for Retail
Apr 18, 2025Unlocking the Power of Ethernet: How It Fuels
Apr 18, 202515 Budget-Friendly Home Remodeling Ideas That Make a
Apr 18, 2025What Should You Know Before Getting Laser Hair
Apr 18, 2025Private Taxi from Birmingham to Manchester Airport
Apr 18, 2025Not Just Pretty – Design a Patio That
Apr 18, 2025Understanding Your CIBIL Score and Its Importance
Apr 18, 2025How Well Does the Intel Arc GPU Perform
Apr 18, 2025Vicdigit Technologies
Apr 18, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Corrugated Boxes
Apr 18, 2025Best Ethernet Cable for Gaming: A Perfect Guide
Apr 17, 2025High-Quality Seat Covers and Mats for Your Car
Apr 17, 2025How to Prepare for Freckles and Blemishes Treatment?
Apr 17, 2025The Top Reasons to Choose Lake Tahoe Boat
Apr 17, 20252031 Industry Report: Key Drivers Fueling the Data
Apr 17, 20259 Scenes Where i7 Laptops Are the Better
Apr 17, 2025Smart Features of Tapmoon Token That You Need
Apr 17, 2025Process Mining Software Market Size to Skyrocket by
Apr 17, 2025Explore a Wide Selection of Smoking Essentials at
Apr 17, 2025Section 125 Tax Savings Plans: What Every Company
Apr 17, 2025Targeted Musculoskeletal Treatment in Edinburgh
Apr 17, 2025How to Layer Skincare with Acne Scar Treatment?
Apr 17, 2025Pizza Novato Is a Must-Try Culinary Experience
Apr 17, 2025How Cloud Solutions in Dubai Are Enabling Remote
Apr 17, 2025How to Get Ready for Your Anti-Aging Facelift
Apr 17, 2025Reliable Solar Panels and Systems for Your Home
Apr 17, 2025Should You Fight for More Disability Benefits and
Apr 17, 2025Modular Office Workstations To Boost Productivity
Apr 17, 2025Find Your Ideal Tech Candidate with EvoTalents
Apr 16, 2025How to Buy a Business in Florida: A
Apr 16, 2025Empowering the Next Generation of Leaders at Lviv
Apr 16, 2025A Vision for the Future of Ukrainian Education
Apr 16, 2025AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud for Hosting
Apr 16, 2025How IV Ozone Helps You Recover Faster from
Apr 16, 2025Why Laundry Services Are Smart for Your Busy
Apr 16, 2025How Hiring an SEO Expert Pays Off for
Apr 16, 2025Decorative LED Lighting for Garden, Backyard & Home
Apr 16, 2025Create Atmosphere with LED Trees & Solar Lights
Apr 16, 2025Comprehensive SEO Services in Dubai: From On-Page to
Apr 16, 2025The Future of Web Design and What It
Apr 16, 2025Transform Your Journey with DNA-Guided Weight Loss
Apr 16, 2025Embrace Wellness at Your Doorstep: The Rise of
Apr 16, 2025Silver Wound Dressing Market Outlook 2031
Apr 16, 2025Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market Analysis 2033
Apr 16, 2025Chronic Disease Management Market Disruption
Apr 16, 2025Medical Gas Equipment Market Strategy Guide
Apr 16, 2025How FSM Software Enhances Technician Productivity
Apr 16, 2025Top 5 Online BIM Courses in 2025: Upskill
Apr 16, 2025Gifts for Boyfriend: What Women Are Asking Online?
Apr 16, 2025Top Real Estate Broker Software to Power Smarter
Apr 16, 2025How a Psychiatrist Can Help You Improve Mental
Apr 16, 2025How to Dress Up or Down the Essentials
Apr 15, 2025How to Choose the Best Audio Recorder for
Apr 15, 2025Why Now Is the Best Time to Explore
Apr 15, 2025Global 3D Printing Gases Market Set to Soar
Apr 15, 2025Mitolyn in New York: Ultimate Guide Weight Loss
Apr 15, 2025Top Reasons to Choose a 4-Star Hotel in
Apr 15, 2025Global Nutritional Analysis Market Set to Soar by
Apr 15, 2025How to Use GMB Everywhere? Complete Guide to
Apr 15, 2025From Romantic Getaways to Paint Nights – Gifting
Apr 15, 2025Top Brightening Face Scrubs to Try in 2025
Apr 15, 2025Vibe Experience Gifts – Adventures, Art, Food &
Apr 15, 2025Taking Care Of Health & Beauty at Our
Apr 15, 2025The Future of Healthcare: Why AI Mobile Apps
Apr 15, 2025Does Body Filler Treatment Require Anesthesia?
Apr 15, 2025Milk Powder Market : Key Drivers, Regional Insights
Apr 15, 2025Benefits of Choosing a Birthing Center in Tulsa
Apr 15, 2025Dump Trucks & Mining Trucks Market : Key
Apr 15, 2025How the Broken Planet Hoodie Scuplts Distinction
Apr 15, 2025Imported Japanese Diapers & Baby Food at Kurumi
Apr 15, 2025Your Trusted Online Shop for Baby Goods from
Apr 15, 2025Understanding the Role of a Neurologist in Treating
Apr 15, 2025Why You Should Host Your Next Event at
Apr 15, 2025Styling Tips for Korean-Inspired Outfits
Apr 15, 2025Anti-Aging Tips Using Natural Ingredients
Apr 15, 2025How’s the Intel i7 vPro Platform Supporting Remote
Apr 15, 2025Recruitment agency in delhi – hirex
Apr 15, 2025Is Natural Cotton Batting the Best Choice for
Apr 15, 2025Private Taxi from Leeds to Manchester Airport –
Apr 15, 2025Best PPC Company in India for Better ROI
Apr 15, 2025How a Top Video Production Agency is Scooping
Apr 15, 2025B2B Payments in 2025: Emerging Trends and Payment
Apr 15, 2025Navigating Global Trade: How Dubai Became a Shipping
Apr 15, 2025Warren Lotas Hoodie: Exclusive Streetwear
Apr 15, 2025Electric Kick Scooter Market : Insights & Forecast
Apr 15, 2025Automotive Paints Market : Insights & Forecast to
Apr 15, 2025Causes of Irregular Periods in Your 30s
Apr 15, 2025Avoiding Common Mistakes When Applying for a Vehicle
Apr 15, 2025Find Premium Home, Beauty, and Health Products at
Apr 15, 2025Shop Quality Products for Every Aspect of Your
Apr 15, 2025Daily Current Affairs in Telugu
Apr 15, 2025Reputable Car Engine Repair: Best Service Practices
Apr 14, 2025MRCOG Part 1 Dates Revealed: What Every Candidate
Apr 14, 2025Is Your Office Lock Jammed? Hire a Locksmith
Apr 14, 2025AZ-104 Exam Dumps: Microsoft Azure Administrator QnA
Apr 14, 2025Why Choosing the Right Audit Company Matters for
Apr 14, 2025Business Travel to Kenya: Visa Rules, Validity, and
Apr 14, 2025Why Spaghetti Strap Blouses Are a Must-Have in
Apr 14, 2025Cheap Taxi from Leeds to Manchester Airport with
Apr 14, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Local SEO for Small
Apr 14, 2025Free 6 Tips: Learn How to Use a
Apr 14, 2025Top Crops for Small-Scale Farming: A Brief Guide
Apr 14, 2025What Are the Key Pieces of Computer Networking
Apr 14, 2025Best Kodi Alternative for iOS in 2025
Apr 14, 2025How do you find the perfect nose shape
Apr 14, 202511 iPhone 12 Case Cover for Nature Lovers
Apr 14, 2025Where to Buy Snore Stop Products Online and
Apr 14, 2025Top Reasons to Choose Thailand for Your Next
Apr 14, 2025Coffee Beans Market is Set to Witness Significant
Apr 14, 2025Snack Food Market is Projected to Reach USD
Apr 14, 2025Vegetable Oil Market to Reach USD 790,878.03 Mn
Apr 14, 2025Abrasive Market Will Achieve USD 63.79 Billion by
Apr 14, 2025Instant wellness? Try home-based IV therapy in Dubai
Apr 14, 2025Are There Programs That Offer Housing Help for
Apr 14, 2025How Noise-Canceling Earbuds Enhance Your Focus
Apr 14, 2025Steps to Purchase from Sp5der Hoodie Brand
Apr 13, 2025MERTRA || Shop Now Mertra Mertra Clothing ||
Apr 13, 2025Understanding Different Types of Teens Counselling
Apr 13, 2025Experience at Hellstar T-Shirt Online Official Store
Apr 13, 2025MERTRA || Shop Now Mertra Mertra Clothing ||
Apr 13, 2025Top 10 Natural Remedies for Insomnia That Help
Apr 13, 2025Where Purpose Meets Action: A Look at Local
Apr 13, 2025How to Find the Right Healthcare Support During
Apr 13, 2025LANVIN® || Lanvin Paris Official Clothing || New
Apr 12, 2025Bape Shirt: Thoughtful Design for Comfort and Style
Apr 12, 2025Ultimate Tips To Boost Your Academic Scores in
Apr 12, 2025The Top 7 Reasons Why Your Car Needs
Apr 12, 2025South Africa Visa Processing Time: What to Expect
Apr 12, 2025Rehydrate, Energize, Glow – All with IV Therapy
Apr 12, 2025Falsely Accused of Domestic Violence? How to Find
Apr 12, 2025Corteiz ® | CRTZRTW Official Website || Sale
Apr 12, 2025Simplify Complex Tasks with MATLAB Assignment Help
Apr 12, 2025Exploring Bare Metal Cloud Market Growth: Trends &
Apr 11, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Quick and Easy Car
Apr 11, 2025Why Use React Helmet for Managing Page Titles
Apr 11, 2025Best Pool Parties in Dubai and Best Beach
Apr 11, 2025Finding the Best Psychologist in Dubai A Guide
Apr 11, 2025Look for Irish Assignment Help Services to Ensure
Apr 11, 2025¿Vale la pena el trasplante de pelo precio?
Apr 11, 2025Tired of Hair Loss? Discover the Magic of
Apr 11, 2025The Importance of Tile Glue and Waterproofing in
Apr 11, 2025Best Therapist in Dubai: Your Guide to Anxiety
Apr 11, 2025Transforming Dubai’s Infrastructure: An Overview
Apr 11, 2025Affordable Stockport Taxis – Book Your Reliable Ride
Apr 11, 2025Handcrafted Eco Baby Toys That Promote Learning |
Apr 11, 2025Saudi Arabia Chiller Market Growth, Key Trends &
Apr 11, 2025Discover Unmatched Comfort at the Best Resorts in
Apr 11, 2025Oman Air Conditioner Market Growth, Key Trends &
Apr 11, 2025Smart Camera Market : Key Drivers, Regional Insights
Apr 11, 2025Middle East and Africa Press Fit Connector Market
Apr 11, 2025Pranav International Oil Mill Machinery
Apr 11, 2025North America Protein Market : Key Drivers, Regional
Apr 11, 2025Do Urinary Tract Infections Lead to Kidney Damage?
Apr 11, 2025Vegan Food Market: Key Drivers, Regional Insights &
Apr 11, 2025Seafood Market : Key Drivers, Regional Insights &
Apr 11, 2025United States Small Kitchen Appliances Market : Key
Apr 11, 2025Mengapa Ligue 1 Jadi Tambang Emas bagi Pemandu
Apr 11, 2025Cortiez Cargos: The Streetwear Staple You Need in
Apr 11, 2025Google Shopping Feed Simprosys – Sync Inventory Fast
Apr 11, 2025Essentials Shorts: Comfort, Style, and Versatility
Apr 11, 2025Protect London® | Protect LDN Clothing Store |
Apr 11, 2025Protect London® | Protect LDN Clothing Store |
Apr 10, 2025Mertra Uk || MertraMertra Clothing || Online Shop
Apr 10, 2025The Best Guide to Home Security Camera Installation
Apr 10, 2025Evisu Shirt: Thoughtful Design for Comfort and Style
Apr 10, 2025Medical Products for Clinics and Hospitals
Apr 10, 2025Denim Tears Shirt: Thoughtful Design for Comfort and
Apr 10, 2025How Long Does SEO Take to Deliver Results?
Apr 10, 2025Saudi Arabia Poultry Meat Market : Key Drivers,
Apr 10, 2025Menswear Market : Key Drivers, Regional Insights &
Apr 10, 2025Fire firms help Abu Dhabi businesses meet safety
Apr 10, 2025Child Care and Development: A Guide for Babysitters
Apr 10, 2025The Importance of a Mattress Protector for Your
Apr 10, 2025Car Insurance Dubai: The Importance of Add-ons
Apr 10, 2025Boost Business Safety & Appeal with Outdoor Lighting
Apr 10, 2025SEO Trends for 2025: What’s Changing?
Apr 10, 2025Best Floodlights Guide for Outdoor Spaces in Qatar
Apr 10, 2025Role of a Premier Security Service Company in
Apr 10, 2025The Importance of Timely Concrete Repair in Dubai’s
Apr 10, 2025IV Therapy in Dubai: The Ultimate Solution for
Apr 10, 2025Best Luxury Hotels In Shimla – A Royal
Apr 10, 2025Challenges Faced by Al Ain Contractors & How
Apr 10, 2025Why Investing in a Quality Gaming Chair in
Apr 10, 2025Why Do Events Need an Ambulance On-Site?
Apr 10, 2025How to Create a Cozy Yet Elegant Living
Apr 10, 2025Which Car Insurance is Mandatory in Abu Dhabi?
Apr 10, 2025How to Choose the Perfect Photo Studio for
Apr 10, 2025Male Infertility: Empowering Men to Seek Help and
Apr 10, 2025Commercial Golf Simulator: Cutting-Edge Technology
Apr 10, 2025How Paint Protection Film Saves Money in the
Apr 10, 2025Sleek & Stylish: The Allure of a Modern
Apr 10, 2025The Benefits of Raw Dog Food Diets: Is
Apr 10, 2025How to Manage Type 2 Diabetes Naturally
Apr 10, 2025How to Maintain Artificial Turf in the UAE’s
Apr 10, 2025How Yas Island is Redefining Sustainable Living in
Apr 10, 2025Top Yoga & Wellness Retreats in Dubai to
Apr 10, 2025Shisha & Fine Dining: Top Abu Dhabi Spots
Apr 10, 2025Choosing a Mobile App Developer in Abu Dhabi:
Apr 10, 20252025 Luxury Real Estate Trends: What Buyers Want
Apr 10, 2025Key Factors to Check Before Buying a Dubai
Apr 10, 2025The Hidden ROI of Custom Software: Beyond Just
Apr 10, 2025How Do You Choose the Perfect Gemstones for
Apr 10, 2025Inside TikTok’s Global Hubs: San Jose to Dubai
Apr 10, 2025Can IV Drips Help with Weight Loss?
Apr 10, 2025New Homes for Sale in Salem, Oregon: Affordable
Apr 10, 2025GV GALLERY® || Raspberry Hills Clothing Store ||
Apr 10, 2025Top Natural Wonders to See in Argentina
Apr 10, 2025Why Jacket Designer Are the Unsung Heroes of
Apr 10, 2025Embrace Culture with Stylish Desi T-Shirts
Apr 10, 2025Eco-Friendly Home Renovation Ideas for Chennai Homes
Apr 10, 2025Why Aluminium Doors & Windows Are Perfect for
Apr 10, 2025Do Dham Yatra by Helicopter – A Divine
Apr 10, 2025Transform Your Floors with Our Carpet Cleaner in
Apr 10, 2025Discover the True Cost of Manaslu Circuit Trekking
Apr 10, 2025Men’s Amethyst Bracelet: Bold, Stylish, and Full of
Apr 10, 2025The Best J.League Stadiums for Live Match Experience
Apr 10, 2025Host Nations That Overachieved at the World Cup
Apr 10, 2025Controversial VAR Decisions That Shook Up World Cup
Apr 10, 2025Reaksi Fan Tergila Setelah Gol di Dunia Football
Apr 10, 2025Вашият път към колата от САЩ започва с
Apr 09, 2025Купете автомобил от САЩ лесно и сигурно с
Apr 09, 2025Бързо и безопасно закупуване на автомобил от САЩ
Apr 09, 2025Търгове на автомобили в САЩ – директно до
Apr 09, 2025The Greatest World Cup Matches of All Time
Apr 09, 2025Top Football Nicknames and the Stories Behind Them
Apr 09, 2025Ride Expert-Tested MTB Routes on Fully Guided Tours
Apr 09, 2025Challenging & Scenic MTB Adventures in Europe and
Apr 09, 2025Royal Enfield Bullet 350 With A Ride Through
Apr 09, 2025Unlock Your Future with ACCA Online Courses in
Apr 09, 202510 Reasons to Work with an Email Marketing
Apr 09, 2025How to Match Socks to Your Outfit: A
Apr 09, 2025Recruitment agency in delhi-hirex
Apr 09, 2025Top 10 Trade Show Stand Design Ideas in
Apr 09, 2025Get Funding From Your Investments with a Loan
Apr 09, 2025Furnished Office for Rent in Dubai
Apr 09, 2025Singapore Airlines Bid for Upgrade – How to
Apr 09, 2025Kombiner sport og natur med de bedste MTB
Apr 09, 2025MTB ture i Danmark og Europa – eventyret
Apr 09, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Corteiz: Corteiz Cargos and
Apr 09, 2025Billionaire Boys Club: A Stylish Journey into Luxury
Apr 09, 202510 Questions to Ask Before Hiring a Roofing
Apr 09, 2025Stay Hydrated & Invincible with IV Drip at
Apr 09, 2025Why Kotlin is the Future of Android App
Apr 09, 2025Corporate Health Insurance vs Individual
Apr 09, 2025Insurance Agent Registration: A Step-by-Step Guide
Apr 08, 2025How a Georgetown Mortgage Broker Can Simplify Your
Apr 08, 2025The Mortgage Renewal Process In Calgary: What Should
Apr 08, 2025How Mortgage Brokers in Calgary Can Help You
Apr 08, 2025Human Touch in a Digital World: How Brands
Apr 08, 2025Membranes Market Estimated to Experience a Hike in
Apr 08, 2025How Can Essay Help Improve Grades
Apr 08, 2025Choosing a transparent aligners clinic: What are the
Apr 08, 2025How a Mobile App Development Company Can Boost
Apr 08, 2025Taxi from Manchester to Gatwick Airport – Reliable,
Apr 08, 2025How to choose the best options for industrial
Apr 08, 2025Find Hope and Healing at Our Texas Mental
Apr 08, 2025Cancer Daily Horoscope: Your Cosmic Guide for the
Apr 08, 20259 Reasons IoT is the Future of Mobile
Apr 08, 2025The Origin and Meaning of the Name Cortiez
Apr 08, 2025Reliable Solar Systems for Your Home and Business
Apr 08, 2025signers for sacoche trapstar
Apr 08, 2025How to Find Affordable and Reliable Maid Services
Apr 08, 2025Is Your PC Smarter Than You Think? Meet
Apr 08, 2025Why Every Business Needs a Barcode for Product
Apr 08, 2025Top Skin Clinic in Pune | Dermatologist &
Apr 08, 2025The Benefits Of A Gear Hob Manufacturers
Apr 08, 2025Refinance Mortgage: A Smart Move for Homeowners
Apr 08, 2025Nizoral 2 Percent Guide and Use – Your
Apr 08, 2025Uses of Sports Nets: Essential Gear for Various
Apr 08, 2025Pulled Hamstring Treatment: How to Heal and Recover
Apr 08, 2025Fast & Reliable Local Window Repair Experts
Apr 07, 2025How Virtual Offices in Tulsa Reshape the Future
Apr 07, 2025Choosing the Right SEO Services in Columbus, Ohio
Apr 07, 2025Your Destination for Japanese Beauty Essentials
Apr 07, 2025Tennis Court Cost: What You Should Expect in
Apr 07, 2025Top 7 Home Buying Mistakes to Avoid in
Apr 07, 2025Securing the Cloud: A Deep Dive into VMware
Apr 07, 2025Custom Stairs and Railings by Ora, Featuring Black
Apr 07, 2025The Pros and Cons of a Tankless Water
Apr 07, 2025Natural Yoga Asanas for Hair Growth and Strength
Apr 07, 2025Sovereign Debt & Emerging Markets
Apr 07, 2025The Ultimate Guide to British IPTV: A Smart
Apr 07, 2025Russia Wine Market Trends Forecast 2025-2033
Apr 07, 2025Elevate Your Style with Pakistani Clothes Online –
Apr 07, 2025Gemini Daily Horoscope: Your Guide to the Stars
Apr 07, 2025Europe Biodiesel Market Trends Forecast 2025-2033
Apr 07, 20253 Ply Single Wall Custom Corrugated Boxes Supplier
Apr 07, 2025Tissue Paper supplier Everything You Need to Know
Apr 07, 2025United States Soup Market Trends Forecast 2025-2033
Apr 07, 2025The Tactical Evolution of RB Leipzig in 2025:
Apr 07, 2025Top 10 Must-See Bundesliga Goals That Define Modern
Apr 07, 2025Achieve a Flatter, Firmer Abdomen with Tummy Tuck
Apr 06, 2025The Pegador Hoodie OF Urban Fashion
Apr 06, 2025Elevate Your Wardrobe with Vertabrae clothing
Apr 06, 2025What Makes Valabasas Jeans So Popular?
Apr 06, 2025What Makes Essentials Clothing So Popular?
Apr 06, 2025Why syna world tracksuit Is a Perfect Summer
Apr 06, 2025Use the Newest Trends from Madhappy sweatpants to
Apr 06, 2025What Makes corteiz clothing So Popular
Apr 06, 2025How to Get Unlimited Lives in Gardenscapes (2024
Apr 06, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Buying the Perfect Puzzle
Apr 06, 2025The Ultimate List of Prehistoric Combat (2024)
Apr 06, 2025The Mortgage Renewal Process in Courtenay: What You
Apr 06, 2025The Mortgage Renewal Process in saint john-What You
Apr 06, 2025No Surgery, Just Shape—Butt & Body Fillers That
Apr 05, 2025How To Prepare For Management Exams
Apr 05, 2025Septic Tank Service Greeley – Professional Cleaning
Apr 05, 2025Jewellery Business in India – SiriusJewels Franchise
Apr 05, 2025Top Realtors in Johnstown | Buy & Sell
Apr 05, 2025Longmont Solar Installation – Save Big with Solar
Apr 05, 2025Essential Tree Maintenance Tips for a Healthier Yard
Apr 05, 2025Glass Repair Denver | Residential & Commercial Glass
Apr 05, 2025Corteiz Clothing Review – Hype or Reality?
Apr 05, 2025Residential Carpet Cleaning – Keep Home Fresh and
Apr 05, 2025Dead Body Ambulance Services in Delhi: Process, Cost
Apr 05, 2025The Most Trusted IVF Centres in Pitampura for
Apr 05, 2025How to Claim Housing Disrepair Compensation in the
Apr 05, 20251977 Essentials Hoodie The Ultimate Comfort
Apr 05, 2025Box Printing in UAE: Your Ultimate Guide to
Apr 05, 2025How to Get Cheap Flights Last Minute: Top
Apr 04, 2025How to Find the Best Body Massage in
Apr 04, 2025The Offsite EMS Lead Auditor Course: Your Next
Apr 04, 2025Pea Protein Market Size, Report and Forecast |
Apr 04, 2025Step Up Your Sustainability Game with ISO 14001
Apr 04, 2025Stata Assignment Help Tips To Overcome Hurdles In
Apr 04, 2025Mitolyn® | Official Website | 100% Natural &
Apr 04, 2025How to Become a Pro Trader with ICFM’s
Apr 04, 202510 Picturesque Spots in Kilkenny to Visit This
Apr 04, 2025Sell Used iPhone 14 for Cash: Get the
Apr 04, 2025Hire a Professional Packers and Movers Service in
Apr 04, 2025Interior & Exterior House Painters in Adelaide: What
Apr 04, 2025Mertra Uk || MertraMertra Clothing || Online Shop
Apr 03, 2025Florist Doreen: Heartfelt Flower Delivery
Apr 03, 2025MERTRA || Shop Now Mertra Mertra Clothing ||
Apr 03, 2025How Assignment Help in Australia Improves Your Study
Apr 03, 2025Order Funeral Flowers in Cyprus – Fast &
Apr 03, 2025The Role of WeldSaver 5 Passport in Modern
Apr 03, 2025Boris Johnson on Global Shifts at AIM Summit
Apr 03, 2025Personal Loan Interest Rate: Factors That Affect How
Apr 03, 2025Microneedling in Los Angeles: The Secret to Flawless
Apr 03, 2025Society in Central Delhi at The Amaryllis by
Apr 03, 2025Join ICFM Best Stock Market Institute for Traders
Apr 03, 2025Healthy Eating is Within Easy Reach With A
Apr 03, 2025Top Benefits of Choosing Home Delivery Food for
Apr 03, 2025Giorgio Milano’s Commitment to Affordable Luxury
Apr 02, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Booklet Printing: How to
Apr 02, 2025Why Ecommerce App Developers are the Backbone of
Apr 02, 2025How to Fundraise for a Cancer Charity in
Apr 02, 2025Taxi Transfers from Carlisle to Manchester Airport –
Apr 02, 2025The Essential Guide to Lock Pins: Uses, Types,
Apr 02, 2025Stay on Top of Your Billing: The Ultimate
Apr 02, 2025DFD: Your Professional Solution for Mold and Fungi
Apr 02, 2025Dates Market: Size, Share, Growth and Forecast |
Apr 02, 2025Infinity Glow: Lab-Created Diamond Wedding Band
Apr 02, 2025Best Movie Sites Like Fmovies for Streaming Movies
Apr 02, 2025How a Computer Course Can Boost Your Resume
Apr 02, 2025Elevate Your Social Media Presence with GSK SMM
Apr 02, 2025How to Make SMART Financial Choices While Purchasing
Apr 02, 2025Core i5 Laptops in Pakistan: The Ultimate Guide
Apr 02, 2025Ultimate Guide to Picking the Perfect Ergo Office
Apr 02, 2025Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Dog Carrying Purse
Apr 02, 2025The Impact of Backlinks on Ecommerce SEO and
Apr 02, 2025The Growing Demand for Fiber Optics in Kenya’s
Apr 02, 2025Top Things to Do in Machu Picchu for
Apr 02, 2025Triund Trek: A Scenic Adventure in the Heart
Apr 01, 2025TDS on Property Purchase from NRI: Key Rules
Apr 01, 2025How to Choose the Right Two-Wheeler Loan Tenure
Apr 01, 2025How Do I Rank My Real Estate Listings
Apr 01, 2025Tax Saving FD Schemes for Senior Citizens
Apr 01, 2025What is NPS? A Complete Guide to the
Apr 01, 2025Send Stunning Flowers Today | BUKETEXPRESS
Apr 01, 2025What are mutual funds, and how do I
Apr 01, 2025Best Pediatric Oral Dental Clinic Near Me: A
Apr 01, 2025Elementor #17783
Apr 01, 2025A Comprehensive Guide To Using Home Loan Calculator
Apr 01, 2025Private Baby Scans in Edinburgh: Everything You Need
Apr 01, 2025Rock Paper Scissors Yellow Dress Trend Uncovered
Apr 01, 2025How Much Does Air Conditioning Repair in Las
Mar 31, 2025How to Choose the Right Fertility Doctor for
Mar 31, 2025Ukrainian Touch: Precision in Every Translation
Mar 31, 2025Neon Sign: A Timeless Trend in Modern Decor
Mar 31, 2025How to Identify Authentic Free Range Eggs at
Mar 31, 2025TAFE Assignment Help – Get Expert Assistance Today!
Mar 31, 2025How Does SAP S/4 HANA Support Human Resources
Mar 31, 2025Honda City: The Epitome of Style, Comfort, and
Mar 31, 2025Say Goodbye To Mascara – Lash Lounge in
Mar 31, 2025The Ultimate White Fox Hoodie Collection You Can’t
Mar 31, 2025Translation Services in Kyiv – Serving Ukraine for
Mar 30, 202550+ Languages with 750+ Skilled Translators
Mar 30, 2025Cooper Jewelry: Merging Tradition with Modern Styles
Mar 30, 202520+ Years of Trusted Translation Expertise in Kyiv
Mar 30, 2025Tout savoir sur l’abonnement Atlas Pro : Le
Mar 30, 2025Manfredi Jewelry’s 30th Anniversary Celebrations
Mar 30, 2025Benison IVF – The Best IVF Centre for
Mar 30, 2025Cost Analysis of Engagement Platforms
Mar 30, 2025Step Guide to Managing Your Server with OpenVZ
Mar 29, 2025Affordable & Quality Rural Universities in India
Mar 29, 2025Global Market of Shot Blasting Machine Manufacturers
Mar 29, 2025How to File a Small Claims Case in
Mar 29, 2025Shot Blasting Machine Manufacturers in India
Mar 29, 2025best exhibition stand designer in dubai
Mar 29, 2025Bad Friend: The Impact of Toxic Friendships
Mar 29, 2025Syna World Beanie: A Deeper Look into the
Mar 29, 2025Window Cleaning Services: Clarity and Shine for Your
Mar 28, 2025HPE Aruba AP-105: Perfect Wireless Access Point for
Mar 28, 2025Education Loan for Your Higher Studies in India
Mar 28, 2025Certificacion gmp: Why It Matters and How to
Mar 28, 2025Are AI Computers the Next Big Thing in
Mar 28, 2025How AI Computers Make Hiring Smarter and Faster
Mar 28, 2025Why an Insulated Patio Cover is the Best
Mar 28, 2025How Podshop Makes It Easy with a London
Mar 28, 2025The Importance of Using a Torque Wrench Socket
Mar 28, 2025The Future of Mobile Apps: Trends Shaping the
Mar 28, 202510 Must-Have Apps for Your Samsung A34 in
Mar 28, 2025The Science Behind the PSYCH-K® Experience: Fact or
Mar 28, 2025Best Laptops in Pakistan – A Comprehensive Guide
Mar 28, 2025How to Apply for ISO Certification Online: A
Mar 28, 2025ISO 9001 Certification: A Game-Changer for Logistics
Mar 28, 2025Off Plan Villa in Dubai: Hidden Investment Gems
Mar 28, 2025Discover Your Dream Home at Eldeco Trinity
Mar 28, 2025Why ISO Training Should Be Your Next Business
Mar 28, 2025Top 5 M4ufree Alternatives for Movie Streaming in
Mar 28, 2025Exploring Rogue Pouches Flavors: A Flavor for Every
Mar 28, 2025“Up In Flames | Up In Flames London
Mar 28, 2025Best Laptops in Pakistan for Every Need and
Mar 28, 2025“Download Tiranga Game – Experience Ultimate Fun and
Mar 28, 2025The Purrfect Accessory for Your Phone
Mar 28, 2025Warehouse Sizes & Costs in Dubai: A Complete
Mar 28, 20257 Reasons AI Enhances Video Game Development
Mar 28, 2025How to Create a Section 125 Plan Document
Mar 28, 2025Why Cereal Packaging Plays a Bigger Role Than
Mar 28, 2025Best Post Construction Cleaning Services, Omaha
Mar 27, 2025Discover Mussoorie, Rishikesh, and Jim Corbett
Mar 27, 2025Navigating Hair Restoration for Women: Your Path to
Mar 27, 2025Luxury 2-Bedroom Homes for Sale in Jumeirah Park
Mar 27, 2025Get Radiant Skin with Charcoal Scrub-Say Goodbye to
Mar 27, 2025Top Benefits of a Cashew Nut Shelling Machine
Mar 27, 2025Are You Trying to Get Better? Examine the
Mar 27, 2025Which Competencies Are Essential for Jobs as Python
Mar 27, 2025MP3Juice: Free Music Downloads and Fast Access to
Mar 27, 2025Top Hair Transplant Clinics in Delhi Finding the
Mar 27, 2025Why Every Koi Pond Needs a Koi Pond
Mar 27, 2025Boost your vitamin D Levels with this 10
Mar 27, 2025The Power of Planning: Utilising a Personal Loan
Mar 27, 2025The Hidden Advantages: Key Benefits of Investing in
Mar 27, 2025Essential Roofing Tips for Contractors & Homeowners
Mar 27, 2025Your Guide to Roof Replacement Costs in St.
Mar 27, 2025Wholesale Socks for All: Shop in Bulk &
Mar 27, 2025Heavy Duty Caster Wheels India: High Load &
Mar 27, 2025Top 7 Best Mortgage Options Offered By Dream
Mar 27, 2025“Regular Cleaning Services in Jenks, OK | T-Town
Mar 27, 2025Protect London || Protect LDN Official Website ||
Mar 27, 2025IV Therapy for Dehydration: A Fast and Effective
Mar 26, 2025How to Get the Best Couples Massage &
Mar 26, 2025Why is Pharma CRM software necessary for success
Mar 26, 2025Best Algo Trading Software India – Quanttrix Review
Mar 26, 2025Software Entwicklung Agentur Berlin
Mar 26, 2025Best Asthma Doctor in Delhi – Expert Care
Mar 26, 2025UPSC Daily Current Affairs Test Series 2025 by
Mar 26, 2025Benefits of Custom Printed PET Cups & Why
Mar 26, 2025Pet Stomach Endoscopy Cost: 10 Ways to Plan
Mar 26, 2025What’s a Simple and Easy Quilt Pattern for
Mar 26, 2025Conservative Podcasts Worth Listening To
Mar 26, 2025Steps to Select the Right Investors Title Insurance
Mar 26, 2025Bots Now Dominate the Web, and That’s a
Mar 26, 2025Taxi from Glasgow to Manchester Airport Transfer
Mar 26, 2025The Ultimate Guide to Finding the Best Internet
Mar 26, 2025Upgrade Your Equipment with Robust Cast Iron Wheels
Mar 26, 2025How a Rotatable Car Phone Holder Improves Navigation
Mar 26, 2025How to Choose the Best Transport Company in
Mar 26, 2025Work-Life Balance Made Easy: from Laila Russian Spa
Mar 26, 2025The Odoo Support Ecosystem: Beyond the Basics
Mar 26, 2025KBH Games Pokemon Red: A Nostalgic Adventure for
Mar 26, 2025Why Does Krunker Keep Closing? Common Causes and
Mar 26, 202510 Reasons Why Turkey Tour is the Perfect
Mar 26, 2025Choosing thе Right Warеhousе Company in Dubai for
Mar 26, 2025Silk Dress: A Luxury Choice for Modern and
Mar 26, 2025Glass Cabinet Care Tips to Keep It Looking
Mar 26, 2025Top 10 Adventure Activities to Try in Leh
Mar 26, 20256 Must-Have Technologies for Modern Gaming Monitors
Mar 26, 2025Test Box Strength with Pacorr’s Compression Tester
Mar 26, 2025Ginny and Georgia Season 3 Plot: Everything You
Mar 26, 2025HP Gaming Laptop: Power and Performance for Gamers
Mar 26, 2025Boost Performance: The Power of a Dedicated Linux
Mar 25, 2025Certification Services in Saudi Arabia
Mar 25, 2025Top 5 Data Analytics Tools for Business Intelligence
Mar 25, 2025Why General Dentistry Is Important for Your Oral
Mar 25, 2025ISO Certification in Pakistan: A Comprehensive Guide
Mar 25, 2025Turning Urban Garden Waste into Green Opportunities
Mar 25, 2025Ace Your Exams with Finance Assignment Help
Mar 25, 2025How to Manage Emergencies During a Leh Ladakh
Mar 25, 2025How to Plan a Scenic Road Trip Through
Mar 25, 2025How to Qualify for a Habitat for Humanity
Mar 25, 2025NAD+ IV Therapy for Hormonal Balance in Dubai
Mar 25, 2025Top 10 Features To Look for in a
Mar 25, 2025Why Penthouses in Qatar Are a Rare Investment
Mar 25, 2025How AI is Changing Recruitment & What Employers
Mar 25, 2025Vinyl vs. Wood Windows: Which is Better for
Mar 25, 2025Make informed decision while choosing to buy best
Mar 25, 2025Choosing the Right Dell 1U Rack Mount Server
Mar 25, 2025Trading on Autopilot: How AI is Reshaping the
Mar 25, 2025Best Multispeciality Hospital in South Delhi
Mar 25, 20256 Reasons to Buy an i5 Gaming Laptop
Mar 25, 2025Download APK Zoom for Laptop – Complete Guide
Mar 25, 2025Boost Your Poetry Career with a Professional Poetry
Mar 25, 2025Choosing the Best Editing Style for Your Athlete
Mar 25, 2025How Intel Arc Works with Intel Core for
Mar 25, 2025Best Massage Therapist in Minneapolis | Relax, Heal
Mar 25, 2025Lightweight vs. Hard-Shell: Which Carry-On is Best?
Mar 25, 2025Gaming Laptops: A Beginner’s Guide to Buying for
Mar 25, 2025What Advantages Do Professional Hair Curlers Offer
Mar 25, 2025Wind Damage on Your Roof? Call a Roofing
Mar 25, 2025The Cost Breakdown of Game Development Services
Mar 25, 2025Saint Vanity | Saint Vanity Shirt || Clothing
Mar 25, 2025Syna World: The UK Streetwear Label Taking Over
Mar 24, 2025Hellstar: The Streetwear Brand Taking Over the Game
Mar 24, 2025Syna World: The Streetwear Empire Shaping UK Fashion
Mar 24, 2025Drama Call: The New Wave of Suspense in
Mar 24, 2025Syna World: The Streetwear Empire Shaping UK Fashion
Mar 24, 2025NOFS: The Game-Changer in Modern Innovation
Mar 24, 2025Syna World: The Streetwear Empire Built by Central
Mar 24, 2025Syna World: The Streetwear Empire Taking Over the
Mar 24, 20255 Common Gym Mistakes & How to Avoid
Mar 24, 2025Everything You Should Know About Dental Implants
Mar 24, 2025Transform Your Business With Expert RPA Consulting
Mar 24, 2025Common challenges in research proposal writing
Mar 24, 2025United States Smart TV Market: Trends, Analysis &
Mar 24, 2025Vegetable Seeds Market : Trends, Analysis & Forecast
Mar 24, 2025Biopsy Devices Market : Trends, Analysis & Forecast
Mar 24, 2025Assessment Help Made Easy: Quality Support for Every
Mar 24, 2025How do you open a savings account online?
Mar 24, 2025United States Ice Cream Market : Trends, Analysis
Mar 24, 2025What Makes a Great Exhibition Stand Builder in
Mar 24, 2025Mexico vs. the U.S.: Why Luxury Homes in
Mar 24, 2025Is the YEEZY GAP Hoodie Worth the Investment or
Mar 24, 2025Discovering the Best Places to Eat in Houston
Mar 24, 2025Exploring Lamb Products: A Culinary Delight
Mar 24, 2025The Psychology Behind Home Visits: Why They Matter
Mar 24, 2025Malaysia Coffee Market : Trends, Analysis & Forecast
Mar 24, 2025Personalized Market By Renub Research
Mar 24, 2025Enhanced Analyst Support Services By Renub Research
Mar 24, 2025Social Research Services By Renub Research
Mar 24, 2025Mystery Audit Services By Renub Research
Mar 24, 2025Développé Épaule pour la Force et la Croissance
Mar 24, 2025Providing the Greatest Online Investing Courses to Investors
Trending Topics
Développé Épaule pour la Force et la Croissance
Développé Épaule pour la Force et la Croissance
The Hidden Power of Local Backlinks for SEO Growth
Everything You Need to Know About Online B.Com Courses
Molded Rubber: A Versatile Material for Industrial and Consumer
Most Reading
Get Latest News from Online Tech Learner
Published Video
Providing the Greatest Online Investing Courses to Investors
Benefits of Hiring Licensed Security Guards in Los Angeles
Développé Épaule pour la Force et la Croissance
International News
Trending Topics
Mystery Audit Services By Renub Research
renubresearchSocial Research Services By Renub Research
renubresearchEnhanced Analyst Support Services By Renub Research
renubresearchWall Painting Services in Qatar: Transform Your Space with Color
paintingservicesDéveloppé Épaule pour la Force et la Croissance Musculaire
The Art of Luxury Interiors: A Journey into Elegance and ComfortMystery Audit Services By Renub Research
renubresearchSocial Research Services By Renub Research
renubresearchEnhanced Analyst Support Services By Renub Research
renubresearchWall Painting Services in Qatar: Transform Your Space with Color
paintingservicesDéveloppé Épaule pour la Force et la Croissance Musculaire
The Art of Luxury Interiors: A Journey into Elegance and ComfortMystery Audit Services By Renub Research
renubresearchProviding the Greatest Online Investing Courses to Investors
In today’s fast-paced financial world, having the right investment knowledge can make all the difference. Many individuals in India are
-
moneyflock / 17 seconds
- 0
- 5 min read
- # Tags
- Eb1 Visa
- Eb1 Visa Cost
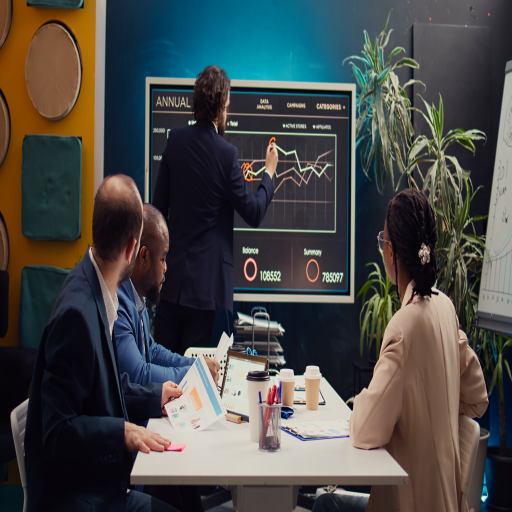
EB1 Requirements Explained – Qualify for Your EB1 Visa Today
No labor certification is required. No job offer or permanent position is needed. Self-petition is allowed. The EB-1A immigrant visas
-
nicksjones / 9 minutes
- 0
- 4 min read
The Best TikTok Video Download Tools for 2025: Save Videos
In 2025, TikTok continues to dominate social media, with millions of videos being uploaded and shared every day. From viral
-
lara14 / 2 hours
- 0
- 5 min read
- # Tags
- custom boxes wholesale
- Custom Packaging
- eco-friendly packaging
- packaging solutions
- printed boxes
How Custom Frozen Pizza Boxes Protect Products During Shipping?
Frozen pizza that comes in custom frozen pizza boxes is important in ensuring the protection of the frozen goods during
-
laxabis174 / 23 hours
- 0
- 6 min read
- # Tags
- custom boxes wholesale
- Custom Packaging
- eco-friendly packaging
- packaging solutions
- printed boxes
Custom Subscription Boxes: The Perfect Packaging of Brands
Custom subscription boxes are a commonplace in the rapidly changing environment of the e-commerce world and provide consumers with an
-
laxabis174 / 23 hours
- 0
- 5 min read
- # Tags
- custom boxes wholesale
- Custom Packaging
- eco-friendly packaging
- packaging solutions
- printed boxes
Custom Die Cuts Boxes: The Ultimate Guide to Smart Packaging
Custom die cut boxes Canada are the most precise, durable, and tailored to the businesses that want to have unique
-
laxabis174 / 23 hours
- 0
- 5 min read
- # Tags
- Jerusalem Real Estate
- jhomes
Comparing Old City vs. Modern Living in Jerusalem Real Estate
Jerusalem, a city where ancient heritage meets modern sophistication, offers a truly unique real estate landscape. Whether you’re drawn to
-
jhomes / 1 day
- 0
- 7 min read
Fire Guard Services in the USA | Protect Lives and Property with Professional Safety Solutions
When it comes to fire safety, prevention and preparedness are non-negotiable. Whether you’re running a construction site, hosting an event,
-
bytebusters / 2 days
- 0
- 6 min read
Benefits of Hiring Licensed Security Guards in Los Angeles
Security is no longer just an optional service for businesses and property owners in Los Angeles. Rising crime rates, busy
-
bytebusters / 2 days
- 0
- 5 min read
The Hidden Power of Local Backlinks for SEO Growth
The fast-paced world of digital is a race for visibility, leads, and credibility for businesses both large and small. Most
-
roilifttechnologies / 2 days
- 0
- 5 min read
- # Tags
- mp3 juice
- mp3juice
- MP3Juice Downloader
MP3Juice vs. YTMP3: Which MP3 Downloader Wins?
In today’s fast-paced digital world, downloading MP3s from YouTube has become incredibly popular. Millions of users rely on online tools
-
mp3juice / 2 days
- 0
- 5 min read
YT5s or SSYouTube: Which Downloader Gives Better Quality?
Downloading YouTube videos has become a common habit for users who love downloading their favorite music, tutorials, and entertainment content
-
sifrasmith / 2 days
- 0
- 4 min read
Rising Importance of Industrial Packaging in Chennai
For decades, Chennai has been regarded as one of India’s most vibrant manufacturing and industrial centers. Home to major automakers, logistics firms, and exporting houses, the city’s need for strong, inexpensive, and effective packing supplies has grown dramatically. Packaging has
-
daniel22kumar / 2 days
- 0
- 8 min read
Rx Propellant’s 9 Lakh Sq. Ft. Lab Spaces in Hyderabad
India’s biotechnology sector is witnessing a transformative shift, powered by innovation, global partnerships, and the demand for advanced life sciences
-
Rxpropellant / 2 days
- 0
- 4 min read
Digital Marketing Strategies for Customer Retention and Upselling
Tone down chasing shiny new leads. Your biggest chance for growth is already right there, sitting in your customer list.
-
fieldpromax / 2 days
- 0
- 8 min read
Selected News
Travel Blogs
Online Voating

This may be the latest case of post aggression emigration in Ukraine. But it is unlikely to be the final stage for millions of people to leave the country. These people do not want


 English
English