[ad_1]
In my early life, I had the opportunity to work as a computer operator, where I had the chance to interact closely with printers.
From inkjet printers to the more advanced color printers, I gained firsthand experience dealing with the intricacies of these indispensable devices.
Throughout my journey, I encountered a range of challenges, including the frustrating realization that the ink cartridge was running low at critical moments, or when the color heads failed to produce the vibrant prints I desired.
Issues such as paper not being properly picked or the dreaded occurrence of multiple pages getting taken by the printer and becoming stubbornly stuck inside became familiar hurdles to overcome.
As my knowledge of printers grew, I found myself diving into the vast world of online research and exploring local markets to find the perfect printer for my needs. The quest for the ideal printer became not just a professional endeavor, but a personal journey filled with valuable insights and lessons learned.


In this article, I aim to share my experiences and knowledge about printers, delving into the fascinating term of these remarkable devices.
We will find the inner workings of printers, explore different types, and discuss their functionalities, advantages, and common challenges.
Whether you are seeking advice on resolving printer issues, understanding the intricacies of printer technologies, or looking for guidance on purchasing a new printer, this article will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips based on my own personal encounters.
Let’s discuss on this journey together, where the world of printers unfolds before us, combining practicality, innovation, and the joy of bringing digital creations into the physical term.
Oh, a close history first!
Who Invented the Printer?
The invention of the printer can be attributed to Johannes Gutenberg, a German goldsmith and inventor who lived in the 15th century.
Gutenberg’s invention revolutionized the process of printing and brought about a significant transformation in the mass production of books.
His most notable invention was the printing press, a mechanical device that enabled the efficient reproduction of written materials.
Before Gutenberg’s invention, books were primarily created by hand, making them expensive and time-consuming to produce.
Gutenberg’s printing press introduced a groundbreaking method that involved using movable type.


This meant that individual letters, numbers, and symbols could be arranged and rearranged to form words and sentences. These movable type pieces were made of metal, usually lead, and could be reused for different printings.
The key component of Gutenberg’s printing press was the printing plate, which held the arranged movable type in place. Ink was applied to the raised surfaces of the type, and then paper was pressed onto the plate, transferring the ink and creating a printed page.
This method allowed for faster, more efficient, and more accurate printing, paving the way for the mass production of books and other printed materials.
Gutenberg’s invention had a profound impact on society, as it made books more accessible and affordable, leading to an increase in literacy and the spread of knowledge.
His printing press laid the foundation for the printers we use today, shaping the history of printing and influencing the development of communication and information dissemination.
History of Various Printers and How They Work
Printers have come a long way since Gutenberg’s invention, continually evolving and incorporating new technologies to improve printing capabilities.
Let’s explore some notable types of printers throughout history:
Dot Matrix Printers:

Dot matrix printers were one of the earliest types of printers and used a matrix of pins to create dots on paper, forming characters and images.
These printers worked by striking an ink-soaked ribbon against the paper, leaving ink impressions in the shape of dots.
Dot matrix printers were known for their reliability and were commonly used for tasks that required multiple copies or carbon forms.
Inkjet Printers:

Inkjet printers are widely used today and work by propelling tiny droplets of ink onto the paper.
These printers operate using ink cartridges that contain liquid ink, which is sprayed through microscopic nozzles onto the paper, creating the desired image or text.
Inkjet printers are versatile, affordable, and capable of producing high-quality prints, making them popular for home use, photo printing, and small office environments.
Laser Printers:

Laser printers utilize laser technology to produce high-quality prints with sharp text and graphics.
In these printers, a laser beam scans across a drum, creating an electrostatic image that attracts toner, a fine powder.
The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, resulting in a permanent print.
Laser printers are known for their fast printing speed, precise output, and suitability for high-volume printing in office environments.
As technology continues to advance, printers have become more sophisticated, offering improved features and capabilities. Today, we have a wide range of printers available, each designed for specific purposes and catering to different printing needs.
Understanding the history and working principles of these printers helps us appreciate the evolution of printing technology and how it has revolutionized communication and information dissemination in our modern world.
Types of Printers – Advantage & Disadvantages
3D Printer
3D printers are innovative devices that create three-dimensional objects by adding successive layers of material. They use various techniques such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), or selective laser sintering (SLS).
3D printers have gained popularity in fields like manufacturing, prototyping, healthcare, and education due to their ability to produce complex and customized objects.


Advantages:
-
- Ability to create three-dimensional objects with complex shapes and customization.
- Widely used in manufacturing, prototyping, healthcare, and education fields.
- Enables cost-effective production of prototypes and small batches of customized products.
Disadvantages:
-
- Relatively slower printing speed compared to traditional printers.
- Limited size and volume of objects that can be printed.
- Higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
AIO (All-in-One) Printer
An AIO printer, also known as a multifunction printer (MFP), combines multiple functions into a single device. It typically includes printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing capabilities.
AIO printers are versatile and space-saving, making them popular choices for home and small office environments.


Advantages:
-
- Combines printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing capabilities in one device.
- Space-saving and convenient for home and small office environments.
- Versatile functionality for various document-related tasks.
Disadvantages:
-
- May have limited printing speed compared to dedicated printers.
- Reliance on a single device for multiple functions, which can be a point of failure.
- Higher upfront cost compared to standalone printers.
Dot Matrix Printer
Dot matrix printers create characters and images by striking a matrix of pins against an ink-soaked ribbon, which transfers ink onto the paper. They produce output by forming dots in patterns, enabling the creation of text and graphics.
Dot matrix printers are known for their reliability and suitability for tasks that require multiple copies or carbon forms.


Advantages:
-
- Reliable and durable for tasks that require multiple copies or carbon forms.
- Suitable for printing on continuous stationery.
- Lower ink or toner costs compared to other printer types.
Disadvantages:
-
- Limited print quality with low-resolution output.
- Noisy operation due to the impact of pins against the ribbon and paper.
- Slower printing speed compared to modern printers.
Inkjet Printer
Inkjet printers work by propelling tiny droplets of ink onto the paper. They operate using ink cartridges that contain liquid ink, which is sprayed through microscopic nozzles onto the paper.
Inkjet printers are versatile, cost-effective, and capable of producing high-quality prints, making them popular for home use, photo printing, and small office environments.


Advantages:
-
- Versatile and cost-effective for home use, photo printing, and small office environments.
- Capable of producing high-quality prints with vibrant colors.
- Compact size and quiet operation.
Disadvantages:
-
- Slower printing speed compared to laser printers.
- Ink cartridges may need frequent replacement and can be expensive.
- Printed documents may be prone to smudging if not allowed to dry properly.
Laser Printer
Laser printers utilize laser technology to produce high-quality prints. They work by scanning a laser beam across a drum, creating an electrostatic image that attracts toner.
The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, resulting in a permanent print.
Laser printers are known for their fast printing speed, sharp text quality, and suitability for high-volume printing.


Advantages:
-
- Fast printing speed and high-volume printing capabilities.
- Sharp text quality with precise details.
- Suitable for office environments and demanding print tasks.
Disadvantages:
-
- Higher upfront cost compared to inkjet printers.
- Larger physical size and weight.
- Limited color printing capabilities.
LED Printer
LED printers are similar to laser printers in terms of their working principle. Instead of using a laser beam to create an electrostatic image, LED printers use an array of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). These LEDs perform the same function as lasers, generating an electrostatic image on the drum.
LED printers offer similar advantages as laser printers, including fast printing speed and high-quality prints.


Advantages:
-
- Offers similar advantages to laser printers, including fast printing speed and high-quality prints.
- Energy-efficient and longer lifespan compared to traditional laser printers.
- Compact size and quiet operation.
Disadvantages:
-
- Less common and may have limited availability compared to laser printers.
- Higher upfront cost compared to inkjet printers.
- Limited color printing capabilities.
MFP (Multifunction Printer)
MFPs, also referred to as all-in-one printers, combine multiple functions into a single device. They typically include printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing capabilities.
MFPs are versatile and convenient, allowing users to perform various tasks without the need for separate devices.


Advantages:
-
- Combines printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing capabilities in one device.
- Versatile and convenient for various document-related tasks.
- Space-saving and cost-effective for home and small office environments.
Disadvantages:
-
- Reliance on a single device for multiple functions, which can be a point of failure.
- May have slower printing speed compared to dedicated printers.
- Higher upfront cost compared to standalone printers.
Plotter
Plotters are printers primarily used for large-format printing, such as architectural blueprints, engineering drawings, or graphical designs. They use a pen or marker to draw continuous lines on paper, providing precise and detailed output.
Plotters are commonly found in engineering, design, and architectural industries.

Advantages:
-
- Precise and detailed output for large-format printing.
- Ideal for architectural blueprints, engineering drawings, and graphical designs.
- High accuracy and capability to handle specialized paper sizes.
Disadvantages:
-
- Limited in terms of document types and applications.
- Slower printing speed compared to traditional printers.
- Higher cost and larger physical size compared to regular printers.
Thermal Printer
Thermal printers use heat to produce images on special thermal paper or labels. They work by selectively heating the paper in specific areas, causing a chemical reaction that results in the formation of the desired image or text.
Thermal printers are widely used in industries such as retail, healthcare, transportation, and ticketing systems due to their fast printing speed and reliability.


Each type of printer offers unique features, advantages, and applications. Understanding these differences can help individuals and businesses choose the most suitable printer for their specific needs and requirements.
Advantages:
-
- Fast printing speed and reliability for industries like retail, healthcare, and transportation.
- No ink or toner required, reducing ongoing costs.
- Ideal for printing receipts, labels, and tickets.
Disadvantages:
-
- Limited to printing on special thermal paper or labels.
- Lack of color printing capability.
- Vulnerable to heat and environmental conditions, which may affect print quality.
Each type of printer offers specific advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to consider factors such as intended use, budget, print quality requirements, and ongoing costs when choosing the most suitable printer for your needs.
Printer Interfaces – Connection Types!
When it comes to connecting a printer to a computer, there are various interfaces or connection types available. These interfaces determine how the printer communicates with the computer.
The most commonly used printer interfaces today include USB cable (wired) and Wi-Fi (wireless).
Let’s explore these interfaces and other connection options in detail:
USB Cable and Port:
-
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a widely used interface for connecting devices, including printers, to computers.
- A USB cable connects the printer to a USB port on the computer.
- USB provides a reliable and high-speed connection, allowing for fast data transfer between the printer and the computer.
Wi-Fi:
-
- Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that enables devices to connect to a local network without the need for physical cables.
- Printers with Wi-Fi capabilities can connect to the computer or other devices over a wireless network.
- This wireless connection allows for convenient printing from multiple devices without the need for direct cable connections.
In addition to USB and Wi-Fi, here is a list of other cables and interfaces that have been used in the past or in specific scenarios:


Cat 5:
-
- Cat 5 (Category 5) cables, also known as Ethernet cables, are commonly used for wired network connections.
- While not as common for directly connecting printers to computers, they may be used in networking setups where printers are shared among multiple computers.
Firewire:
-
- Firewire (IEEE 1394) is an interface that was popular for high-speed data transfer between devices.
- It was commonly used for connecting devices like external hard drives or video cameras, but it is less prevalent in printer connections today.
MPP-1150:
-
- MPP-1150 (Miniature Printer/Plotter) is a specialized interface used for connecting certain types of printers and plotters.
Parallel Port:
-
- Parallel ports were once commonly used to connect printers to computers.
- They allowed for bi-directional communication and higher data transfer rates compared to older serial ports.
- However, parallel ports have become less common as USB and other interfaces have gained popularity.
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface):
-
- SCSI is an older interface used for connecting various devices, including printers, scanners, and storage devices.
- It provided high-speed data transfer rates and flexibility in device connectivity.
- However, SCSI is less commonly used in modern printer connections.
Serial Port:
-
- Serial ports were used for connecting printers to computers in the past.
- They allowed for serial communication, but their slower data transfer rates and limitations in terms of device compatibility have made them less prevalent today.
It’s important to note that the availability of specific interfaces may vary depending on the printer model and the computer’s hardware. It’s always recommended to check the printer’s specifications and the computer’s connectivity options to ensure compatibility.
How Printers Work?
Printers are intricate devices that rely on a combination of hardware and software components to carry out their printing functions.
Understanding how printers work involves delving into the various steps and processes involved in creating printed output.
Let’s explore the detailed explanation of the printer’s operation:
Data Processing:
The printing process begins with the printer receiving data from a connected device, such as a computer or mobile device.
This data can be in the form of text, images, or other printable content.
The printer’s internal circuitry, which includes a processor and memory, processes the received data. The data is converted into a printable format that the printer can interpret and reproduce on paper.
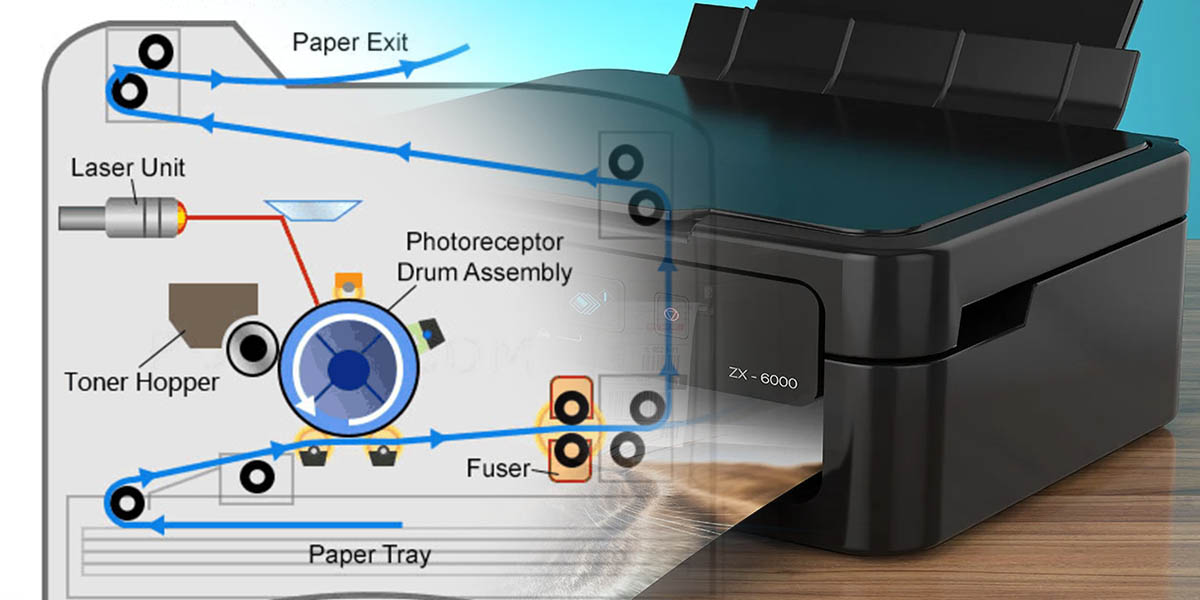

Image Formation:
Once the data has been processed, the printer begins the image formation process. The specific method of image formation depends on the type of printer, whether it’s an inkjet printer, laser printer, or another type.
In an inkjet printer, the printer head moves back and forth across the paper, depositing tiny droplets of ink in a precise pattern.
In a laser printer, a laser beam scans across a drum, creating an electrostatic image that attracts toner, which is then transferred onto the paper.
Other types of printers, such as dot matrix printers or thermal printers, have their own unique methods of image formation.
Paper Handling:
The printer incorporates mechanisms to handle paper and ensure its accurate positioning and smooth movement.
Paper is typically stored in a paper tray or cassette, from which the printer draws the sheets one at a time. Various components, such as feed rollers, guides, and sensors, work together to control the movement of paper through the printer.
The printer carefully aligns the paper to ensure proper registration of the printed content.
Some printers support different paper sizes or types, allowing for flexibility in printing various document formats.
Output Delivery:
Once the printing process is complete, the printer delivers the printed output to an output tray or another designated location.
The printed sheets are stacked in an orderly manner to prevent mixing or smudging of the freshly printed content. In some printers, especially those with multiple trays or advanced finishing options, the output can be sorted, collated, or stapled.
Depending on the printer model and settings, the output tray may have additional features like paper capacity indicators or automatic paper ejection.
It’s important to note that printers can have additional features and functionalities specific to their type and model.
These can include duplex printing (printing on both sides of the paper), borderless printing for photos, wireless connectivity options, and more. Each type of printer follows its own set of processes and utilizes specific technologies to achieve the desired printing results.
What Is the Most Commonly Used Printer?
Inkjet printers are among the most commonly used printers today. They are popular for home and small office use due to their affordability and versatility.
Inkjet printers can produce high-quality prints, making them suitable for various applications, including document printing, photo printing, and graphic design.
Do I Need a Printer with My Computer?
The need for a printer with a computer depends on individual requirements. While many tasks can be done digitally, having a printer offers several advantages. It allows for the creation of physical copies, making it easier to review, share, or archive documents.
Additionally, having a printer at hand provides convenience and eliminates the need for external printing services.


Does a Printer Require a Computer to Be Used?
No, printers do not always require a computer to be used. Many modern printers offer additional features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing for direct printing from smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices.
These printers can receive print commands wirelessly, making them more versatile and convenient to use.
Does a Computer Printer Have Memory?
Yes, computer printers may have memory capabilities. Some printers feature onboard memory that allows them to store print jobs temporarily.
This can be useful in cases where multiple users send print jobs simultaneously, as the printer can queue and process them in the order received.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between inkjet and laser printers?
Inkjet printers use liquid ink sprayed onto the paper, while laser printers use toner and a laser beam to produce prints. Inkjet printers are generally more affordable, while laser printers offer faster printing speeds and sharper text quality.
Can I print wirelessly from my mobile device?
Yes, many modern printers support wireless connectivity, allowing you to print directly from your smartphone or tablet using apps or built-in printing features.
How do I maintain my printer?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning the print heads, replacing ink or toner cartridges when empty, and keeping the printer’s interior free from dust and debris. Consult your printer’s user manual for specific instructions.
Are there eco-friendly printer options available?
Yes, there are eco-friendly printers that use energy-saving features and offer options for recycled paper and duplex printing (printing on both sides of the paper).
Can I print documents from the cloud using a printer?
Many modern printers support cloud printing, allowing you to print documents directly from cloud storage services such as Google Drive or Dropbox.
Are all-in-one printers suitable for professional use?
Yes, all-in-one printers can handle professional tasks effectively, including printing, scanning, and copying.
Can I use laser printers for color printing?
While laser printers are primarily known for black and white printing, some models offer color printing capabilities.
How often should I replace ink cartridges in an inkjet printer?
The frequency of replacing ink cartridges depends on your usage. Generally, it is recommended to replace them when the ink runs low or quality begins to degrade.
Can printers connect to wireless networks?
Yes, many modern printers offer wireless connectivity, allowing you to print documents wirelessly from your computer or mobile devices.
Do laser printers require special paper?
Laser printers can work with a wide range of paper types, but for optimal results, it is recommended to use paper specifically designed for laser printing.
[ad_2]
Source link





1 Comment